Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Colon
P3650 - Artificial Intelligence-Aided Colonoscopy Does Not Improve Endoscopist Performance in Community Settings
Tuesday, October 29, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E

- PK
Pujan N. Kandel, MD
HCA Florida Citrus Memorial Hospital
Hernando, FL
Presenting Author(s)
Pujan N. Kandel, MD1, Vamsee Mupparaju, MD2, Kashin Mathur, BS3, Varun Patel, MD4, Trupti Shinde, MD4, Sreekanth Chandrupatla, MD4
1HCA Florida Citrus Memorial Hospital, Hernando, FL; 2HCA Florida Healthcare Citrus Memorial Hospital, Inverness, FL; 3Emory University, Atlanta, GA; 4HCA Florida Citrus Hospital, Inverness, FL
Introduction: Artificial intelligence aided colonoscopy has demonstrated decrease in adenoma miss rate and increase in ADR and adenoma per colonoscopy (APC) in several randomized controlled trials. The first CADe (Computer aided detection) first approved in the United States was GI Genius (GI Genius, Medtronic, Minneapolis, MN). Most of the studies are done at large academic centers. There is a small amount of data on whether this CADe application is useful among community gastroenterologists. We conducted this study to evaluate the effectiveness of CADe application (GI Genius) in community settings with regards to ADR and APC detection.
Methods: The study was approved by the HCA Citrus Memorial Hospital institutional review board . Informed consent was obtained from all patients for the standard procedure. All colonoscopy performed from April 2022 to April 2024 were reviewed through the GI QuIc database. We only included patients who underwent first time screening colonoscopy. We compared the colonoscopy data one year before installation of GI Genius (April 2022-April 2023, Pre GI-Genius group) and after one year (Mid-April 2023- April 2024, Post GI Genius group). Statistical analysis was carried out using JMP (v10, SAS Institute Inc, North Carolina, USA) software. The main objective of this study was to compare ADR before GI Genius and after GI Genius.
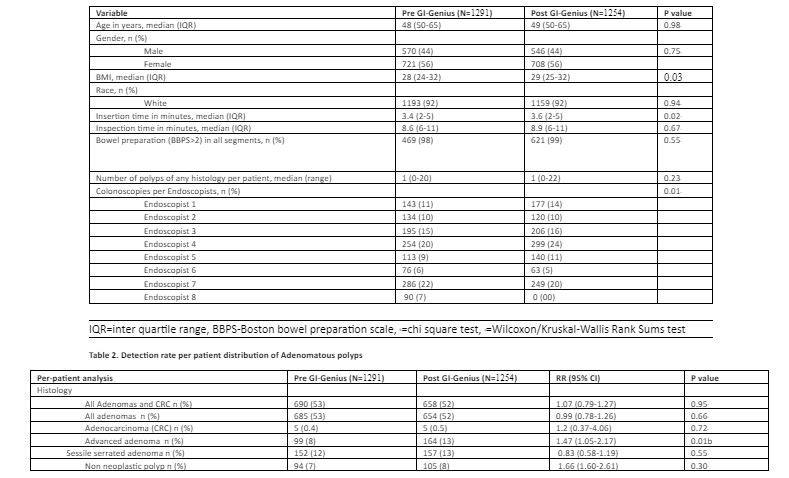
Results: Of the total 2545 patients included in the study, 51% (n=1291) patients were from the Pre-GI Genius group and 49% (n=1254) from the Post-GI Genius group. Both groups were similar with regards to age, race, gender, median withdrawal time, BBPS >2 scores, except BMI, number of polyps of any histology and endoscopist colonoscopies. Median insertion time was significantly higher on the Post-GI Genius group (Table 1). After adjusting for age, gender, BMI, endoscopist; adenoma detection rate (ADR) was similar in both the groups; Pre-GI Genius group (690/1291, 53%) vs Post GI Genius group (658/1254, 51%); [RR, 1.07; 95% CI, 0.79-1.27). Similarly, there was no difference in serrated adenoma detection rate among both the groups; Pre-GI Genius group (65/478, 14%) vs Post GI Genius group (73/630, 11%); [RR, 0.83; 95% CI, 0.58-1.19). However, a significantly higher number of advanced adenomas were detected in the Post GI Genius group (Table 2).
Discussion: In our study there was no improvement in ADR with CADe assisted colonoscopy from baseline. Further studies are needed to confirm this finding.
Disclosures:
Pujan N. Kandel, MD1, Vamsee Mupparaju, MD2, Kashin Mathur, BS3, Varun Patel, MD4, Trupti Shinde, MD4, Sreekanth Chandrupatla, MD4. P3650 - Artificial Intelligence-Aided Colonoscopy Does Not Improve Endoscopist Performance in Community Settings, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1HCA Florida Citrus Memorial Hospital, Hernando, FL; 2HCA Florida Healthcare Citrus Memorial Hospital, Inverness, FL; 3Emory University, Atlanta, GA; 4HCA Florida Citrus Hospital, Inverness, FL
Introduction: Artificial intelligence aided colonoscopy has demonstrated decrease in adenoma miss rate and increase in ADR and adenoma per colonoscopy (APC) in several randomized controlled trials. The first CADe (Computer aided detection) first approved in the United States was GI Genius (GI Genius, Medtronic, Minneapolis, MN). Most of the studies are done at large academic centers. There is a small amount of data on whether this CADe application is useful among community gastroenterologists. We conducted this study to evaluate the effectiveness of CADe application (GI Genius) in community settings with regards to ADR and APC detection.
Methods: The study was approved by the HCA Citrus Memorial Hospital institutional review board . Informed consent was obtained from all patients for the standard procedure. All colonoscopy performed from April 2022 to April 2024 were reviewed through the GI QuIc database. We only included patients who underwent first time screening colonoscopy. We compared the colonoscopy data one year before installation of GI Genius (April 2022-April 2023, Pre GI-Genius group) and after one year (Mid-April 2023- April 2024, Post GI Genius group). Statistical analysis was carried out using JMP (v10, SAS Institute Inc, North Carolina, USA) software. The main objective of this study was to compare ADR before GI Genius and after GI Genius.
Results: Of the total 2545 patients included in the study, 51% (n=1291) patients were from the Pre-GI Genius group and 49% (n=1254) from the Post-GI Genius group. Both groups were similar with regards to age, race, gender, median withdrawal time, BBPS >2 scores, except BMI, number of polyps of any histology and endoscopist colonoscopies. Median insertion time was significantly higher on the Post-GI Genius group (Table 1). After adjusting for age, gender, BMI, endoscopist; adenoma detection rate (ADR) was similar in both the groups; Pre-GI Genius group (690/1291, 53%) vs Post GI Genius group (658/1254, 51%); [RR, 1.07; 95% CI, 0.79-1.27). Similarly, there was no difference in serrated adenoma detection rate among both the groups; Pre-GI Genius group (65/478, 14%) vs Post GI Genius group (73/630, 11%); [RR, 0.83; 95% CI, 0.58-1.19). However, a significantly higher number of advanced adenomas were detected in the Post GI Genius group (Table 2).
Discussion: In our study there was no improvement in ADR with CADe assisted colonoscopy from baseline. Further studies are needed to confirm this finding.

Figure: Table 1 Patient characteristics Table 2. Detection rate per patient distribution of Adenomatous polyps
b=chi square test, a=Wilcoxon/Kruskal-Wallis Rank Sums test, RR=relative risk, CI= confidence interval, CRC=colorectal cancer, advanced adenoma=an adenoma of 10mm or larger, or as an adenoma (irrespective of size) with at least 20% villous histology or with high-grade dysplasia
b=chi square test, a=Wilcoxon/Kruskal-Wallis Rank Sums test, RR=relative risk, CI= confidence interval, CRC=colorectal cancer, advanced adenoma=an adenoma of 10mm or larger, or as an adenoma (irrespective of size) with at least 20% villous histology or with high-grade dysplasia
Disclosures:
Pujan Kandel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vamsee Mupparaju indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kashin Mathur indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Varun Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Trupti Shinde indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sreekanth Chandrupatla indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Pujan N. Kandel, MD1, Vamsee Mupparaju, MD2, Kashin Mathur, BS3, Varun Patel, MD4, Trupti Shinde, MD4, Sreekanth Chandrupatla, MD4. P3650 - Artificial Intelligence-Aided Colonoscopy Does Not Improve Endoscopist Performance in Community Settings, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
