Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Colon
P3651 - Impact of Liver Transplantation on Colorectal Cancer Development in PSC-IBD Patients
Tuesday, October 29, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio
- GC
Gerardo Calderon, MD
Mayo Clinic
Rochester, MN
Presenting Author(s)
Gerardo Calderon, MD, Karina Sato-Espinoza, , Laura Kek, MD, MS, Konstantinos N. Lazaridis, MD, Nayantara Coelho-Prabhu, MD, FACG
Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN
Introduction: Inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) are associated with an increased risk of colorectal cancer (CRC), particularly in patients with concomitant primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC). It is unclear which factors are related to the increased risk in the PSC-IBD cohort. We aim to characterize the endoscopic and histologic findings that precede CRC development in PSC-IBD patients.
Methods: A database of PSC-IBD patients seen at Mayo Clinic Rochester between 1990 and 2023 was utilized. Our study included PSC-IBD patients who developed CRC and had at least one colonoscopy within 5 years before CRC diagnosis. We extracted demographic data, IBD duration, CRC diagnosis and location, colonoscopy and pathology reports, and liver transplant status. Right-sided CRC included the cecum, ascending colon, and transverse colon, while left-sided CRC included the descending colon, sigmoid colon, and rectum. Endoscopic scoring was assigned to each segment based on the severity of inflammation: no inflammation (0), mild (1), moderate (2), and severe (3). Similarly, histologic scoring was assigned based on the degree of inflammation: normal (0), quiescent (1), mild (2), moderate (3), and severe (4). Average endoscopic and histologic scores for all colonic segments were calculated. Statistical analysis included Student’s t-test for continuous variables and the chi-squared test for categorical data.
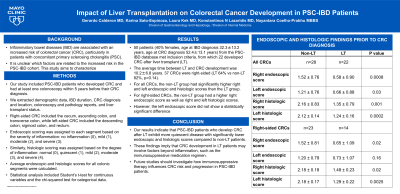
Results: 50 patients (40% females, age at IBD diagnosis 32.3±13.2 years, age at CRC diagnosis 52.4±13.1 years) from the PSC-IBD database met inclusion criteria, from which 22 developed CRC after liver transplant (LT). The average time between LT and CRC development was 10.2±6.8 years. 37 CRCs were right-sided (LT 64% vs non-LT 82%, p=0.14). For all CRCs, the non-LT group had significantly higher right and left endoscopic and histologic scores than the LT group. For right-sided CRCs, the non-LT group had a higher right endoscopic score as well as right and left histologic scores. However, the left endoscopic score did not show a statistically significant difference.
Discussion: Our results indicate that PSC-IBD patients who develop CRC after LT exhibit more quiescent disease with significantly lower endoscopic and histologic scores compared to non-LT patients. These findings imply that CRC development in LT patients may involve factors beyond inflammation, such as the immunosuppressive regimen. Future studies should investigate how immunosuppressive therapy influences CRC risk and progression in PSC-IBD patients.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Gerardo Calderon, MD, Karina Sato-Espinoza, , Laura Kek, MD, MS, Konstantinos N. Lazaridis, MD, Nayantara Coelho-Prabhu, MD, FACG. P3651 - Impact of Liver Transplantation on Colorectal Cancer Development in PSC-IBD Patients, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN
Introduction: Inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) are associated with an increased risk of colorectal cancer (CRC), particularly in patients with concomitant primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC). It is unclear which factors are related to the increased risk in the PSC-IBD cohort. We aim to characterize the endoscopic and histologic findings that precede CRC development in PSC-IBD patients.
Methods: A database of PSC-IBD patients seen at Mayo Clinic Rochester between 1990 and 2023 was utilized. Our study included PSC-IBD patients who developed CRC and had at least one colonoscopy within 5 years before CRC diagnosis. We extracted demographic data, IBD duration, CRC diagnosis and location, colonoscopy and pathology reports, and liver transplant status. Right-sided CRC included the cecum, ascending colon, and transverse colon, while left-sided CRC included the descending colon, sigmoid colon, and rectum. Endoscopic scoring was assigned to each segment based on the severity of inflammation: no inflammation (0), mild (1), moderate (2), and severe (3). Similarly, histologic scoring was assigned based on the degree of inflammation: normal (0), quiescent (1), mild (2), moderate (3), and severe (4). Average endoscopic and histologic scores for all colonic segments were calculated. Statistical analysis included Student’s t-test for continuous variables and the chi-squared test for categorical data.
Results: 50 patients (40% females, age at IBD diagnosis 32.3±13.2 years, age at CRC diagnosis 52.4±13.1 years) from the PSC-IBD database met inclusion criteria, from which 22 developed CRC after liver transplant (LT). The average time between LT and CRC development was 10.2±6.8 years. 37 CRCs were right-sided (LT 64% vs non-LT 82%, p=0.14). For all CRCs, the non-LT group had significantly higher right and left endoscopic and histologic scores than the LT group. For right-sided CRCs, the non-LT group had a higher right endoscopic score as well as right and left histologic scores. However, the left endoscopic score did not show a statistically significant difference.
Discussion: Our results indicate that PSC-IBD patients who develop CRC after LT exhibit more quiescent disease with significantly lower endoscopic and histologic scores compared to non-LT patients. These findings imply that CRC development in LT patients may involve factors beyond inflammation, such as the immunosuppressive regimen. Future studies should investigate how immunosuppressive therapy influences CRC risk and progression in PSC-IBD patients.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Gerardo Calderon indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Karina Sato-Espinoza indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Laura Kek indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Konstantinos N. Lazaridis indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nayantara Coelho-Prabhu: Iterative Health – Advisory Committee/Board Member.
Gerardo Calderon, MD, Karina Sato-Espinoza, , Laura Kek, MD, MS, Konstantinos N. Lazaridis, MD, Nayantara Coelho-Prabhu, MD, FACG. P3651 - Impact of Liver Transplantation on Colorectal Cancer Development in PSC-IBD Patients, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
