Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Colon
P3727 - Concurrent Takayasu Arteritis and Inflammatory Bowel Disease in a Patient Presenting With Acute Vision Loss
Tuesday, October 29, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Priyanka Jagannathan, MD
University of Texas at Austin Dell Medical School
Austin, TX
Presenting Author(s)
Priyanka Jagannathan, MD, Youssef Abdullah, MD, Hamzah Ali, MD
University of Texas at Austin Dell Medical School, Austin, TX
Introduction: In this case report we discuss the uncommon concurrence of Takayasu arteritis and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) in a patient presenting with vision loss.
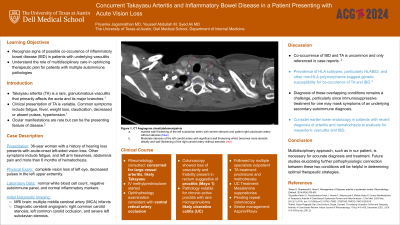
Case Description/Methods: A 36-year-old woman with a history of bilateral hearing loss presented to the emergency with acute-onset left-sided vision loss. Associated symptoms included left arm heaviness, fatigue, muscle stiffness, abdominal bloating, and intermittent bloody stools. On examination, she was afebrile and found to have complete vision loss in the left eye with decreased pulses in the left upper extremity. Laboratory studies revealed a normal white blood cell count, negative autoimmune panel, and normal inflammatory markers. Her brain MRI was notable for scattered infarcts in the left middle cerebral artery territory. CT Angiogram showed multivessel wall thickening and several areas of marked stenosis in the left common carotid artery. Based on these results, there was concern for Takayasu arteritis and she received empiric treatment with methylprednisolone. Due to her gastroenterological symptoms, she underwent a lower endoscopy which revealed proctitis. Pathology of rectal mucosa showed variably increased inflammation in the lamina propria with areas of acute cryptitis and crypt abscesses, suggestive of ulcerative colitis. She was discharged from the hospital with a steroid course and plan for outpatient gastroenterology and rheumatology follow-up.
Discussion: Takayasu arteritis (TA) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) are both chronic inflammatory disorders with complex pathophysiologies. The co-occurrence of these two conditions is uncommon and referenced in the literature only in case reports1. Recent studies have suggested that shared genetic susceptibility, such as NOD2/CARD15 polymorphisms, may contribute to the co-occurrence of TA and IBD, particularly Crohn's disease2. Diagnosis of these overlapping conditions remains a challenge, particularly since immunosuppressive treatment for one may mask symptoms of an underlying secondary autoimmune diagnosis.
Our case highlights the complex presentation of these inflammatory disorders and the need for a multidisciplinary approach to diagnosis and management. Further research is needed to elucidate the pathophysiological links between these conditions and to develop optimal therapeutic strategies for patients with co-occurring TA and IBD.
Disclosures:
Priyanka Jagannathan, MD, Youssef Abdullah, MD, Hamzah Ali, MD. P3727 - Concurrent Takayasu Arteritis and Inflammatory Bowel Disease in a Patient Presenting With Acute Vision Loss, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
University of Texas at Austin Dell Medical School, Austin, TX
Introduction: In this case report we discuss the uncommon concurrence of Takayasu arteritis and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) in a patient presenting with vision loss.
Case Description/Methods: A 36-year-old woman with a history of bilateral hearing loss presented to the emergency with acute-onset left-sided vision loss. Associated symptoms included left arm heaviness, fatigue, muscle stiffness, abdominal bloating, and intermittent bloody stools. On examination, she was afebrile and found to have complete vision loss in the left eye with decreased pulses in the left upper extremity. Laboratory studies revealed a normal white blood cell count, negative autoimmune panel, and normal inflammatory markers. Her brain MRI was notable for scattered infarcts in the left middle cerebral artery territory. CT Angiogram showed multivessel wall thickening and several areas of marked stenosis in the left common carotid artery. Based on these results, there was concern for Takayasu arteritis and she received empiric treatment with methylprednisolone. Due to her gastroenterological symptoms, she underwent a lower endoscopy which revealed proctitis. Pathology of rectal mucosa showed variably increased inflammation in the lamina propria with areas of acute cryptitis and crypt abscesses, suggestive of ulcerative colitis. She was discharged from the hospital with a steroid course and plan for outpatient gastroenterology and rheumatology follow-up.
Discussion: Takayasu arteritis (TA) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) are both chronic inflammatory disorders with complex pathophysiologies. The co-occurrence of these two conditions is uncommon and referenced in the literature only in case reports1. Recent studies have suggested that shared genetic susceptibility, such as NOD2/CARD15 polymorphisms, may contribute to the co-occurrence of TA and IBD, particularly Crohn's disease2. Diagnosis of these overlapping conditions remains a challenge, particularly since immunosuppressive treatment for one may mask symptoms of an underlying secondary autoimmune diagnosis.
Our case highlights the complex presentation of these inflammatory disorders and the need for a multidisciplinary approach to diagnosis and management. Further research is needed to elucidate the pathophysiological links between these conditions and to develop optimal therapeutic strategies for patients with co-occurring TA and IBD.
Disclosures:
Priyanka Jagannathan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Youssef Abdullah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hamzah Ali indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Priyanka Jagannathan, MD, Youssef Abdullah, MD, Hamzah Ali, MD. P3727 - Concurrent Takayasu Arteritis and Inflammatory Bowel Disease in a Patient Presenting With Acute Vision Loss, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
