Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Colorectal Cancer Prevention
P3873 - Association of Klebsiella pneumoniae Liver Abscess With Colonic Adenoma: A Case Report
Tuesday, October 29, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Dongmin Shin, MD
BronxCare Health System
Bronx, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Dongmin Shin, MD1, Sameer Kandhi, MD1, Franklin Sosa, MD1, Nikhitha Mantri, MD1, Ali Ghazanfar, MBBS2, Jasbir Makker, MD1, Harish Patel, MD1
1BronxCare Health System, Bronx, NY; 2Fauji Foundation Hospital, Rawalpindi, Punjab, Pakistan
Introduction: Pyogenic liver abscess frequently stem from hepatobiliary tract disorders or intra-abdominal infections, including cholecystitis, suppurative cholangitis, suppurative pyelphlebitis, appendicitis, diverticulitis, and peritonitis. Recent studies have highlighted a potential association between Klebsiella pneumoniae-induced liver abscess and colon cancer. In this case-report we delineate the correlation between pyogenic liver abscess due to Klebsiella pneumoniae and colonic polyps.
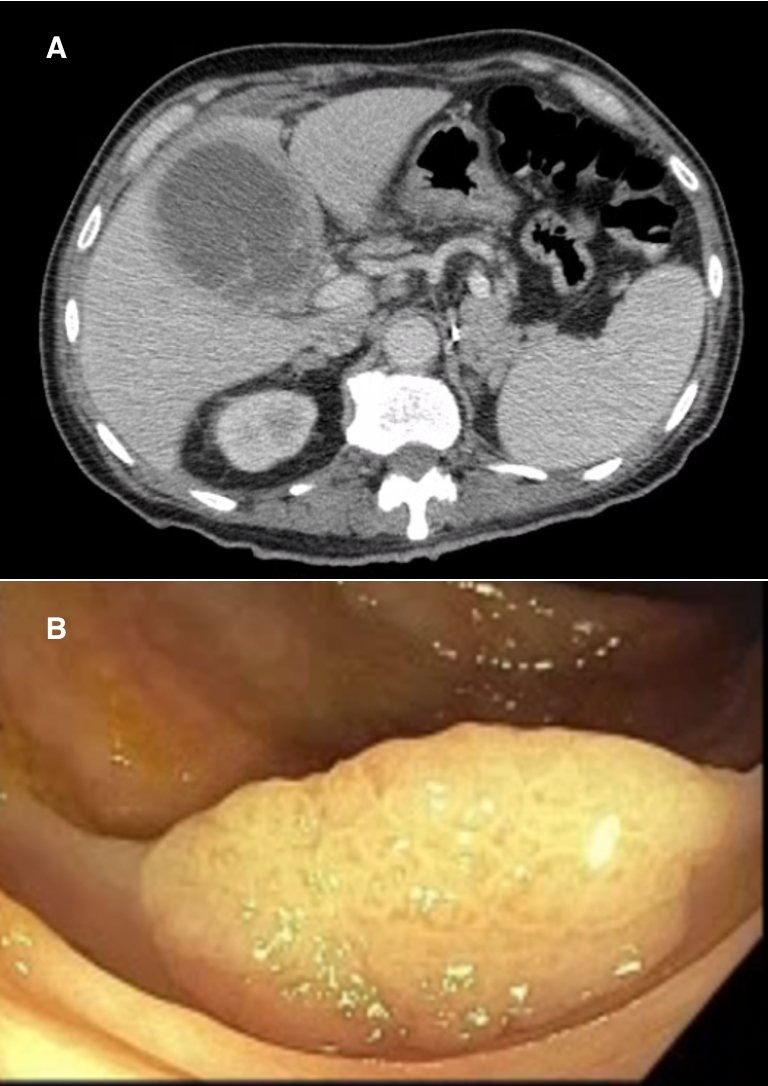
Case Description/Methods: A 76-year-old male with a history of hypertension, hepatitis C, renal cell carcinoma, and left nephrectomy presented with a three-week history of abdominal discomfort. Laboratory analysis revealed leukocytosis of 14.4K/microL, with normal liver function tests. Initial abdominal computed tomography (CT) imaging revealed a 5x10 cm collection in the right lobe of the liver (Figure A) adjacent to the gallbladder, exerting pressure on the common bile duct with mild intrahepatic ductal dilatation. Ultrasound of the abdomen and magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) did not reveal any gallbladder stone, cholecystitis, or biliary stone. The collection was drained percutaneously and the purulent aspirate grew Klebsiella pneumoniae. Due to the inconclusive etiology of the liver abscess, colonoscopy was performed to explore potential colonic malignancies. The patient had no family history of colon cancer and had a colonoscopy done 10 years ago which was negative for colon polyps. However, the colonoscopic examination this time revealed multiple colonic polyps, with the largest measuring 20 mm (Figure B). Patient was treated with intravenous antibiotics for the liver abscess, which was attributed to the presence of colonic polyps. It is postulated that colon cancer or adenoma-associated mucosal defects may facilitate bacterial infiltration into the portal circulation, thereby contributing to hepatic seeding and subsequent liver abscess formation.
Discussion: Pyogenic liver abscess associated with Klebsiella pneumoniae are commonly observed in individuals with concurrent diabetes mellitus and advanced age. In cases lacking evident hepatobiliary or intra-abdominal infections, which typically serve as primary sources of bacterial dissemination, the etiology of liver abscess often remains cryptogenic. However, it is essential to consider colonic adenoma or carcinoma as potential underlying causes in those with pyogenic liver abscess and warrants investigation.
Disclosures:
Dongmin Shin, MD1, Sameer Kandhi, MD1, Franklin Sosa, MD1, Nikhitha Mantri, MD1, Ali Ghazanfar, MBBS2, Jasbir Makker, MD1, Harish Patel, MD1. P3873 - Association of Klebsiella pneumoniae Liver Abscess With Colonic Adenoma: A Case Report, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1BronxCare Health System, Bronx, NY; 2Fauji Foundation Hospital, Rawalpindi, Punjab, Pakistan
Introduction: Pyogenic liver abscess frequently stem from hepatobiliary tract disorders or intra-abdominal infections, including cholecystitis, suppurative cholangitis, suppurative pyelphlebitis, appendicitis, diverticulitis, and peritonitis. Recent studies have highlighted a potential association between Klebsiella pneumoniae-induced liver abscess and colon cancer. In this case-report we delineate the correlation between pyogenic liver abscess due to Klebsiella pneumoniae and colonic polyps.
Case Description/Methods: A 76-year-old male with a history of hypertension, hepatitis C, renal cell carcinoma, and left nephrectomy presented with a three-week history of abdominal discomfort. Laboratory analysis revealed leukocytosis of 14.4K/microL, with normal liver function tests. Initial abdominal computed tomography (CT) imaging revealed a 5x10 cm collection in the right lobe of the liver (Figure A) adjacent to the gallbladder, exerting pressure on the common bile duct with mild intrahepatic ductal dilatation. Ultrasound of the abdomen and magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) did not reveal any gallbladder stone, cholecystitis, or biliary stone. The collection was drained percutaneously and the purulent aspirate grew Klebsiella pneumoniae. Due to the inconclusive etiology of the liver abscess, colonoscopy was performed to explore potential colonic malignancies. The patient had no family history of colon cancer and had a colonoscopy done 10 years ago which was negative for colon polyps. However, the colonoscopic examination this time revealed multiple colonic polyps, with the largest measuring 20 mm (Figure B). Patient was treated with intravenous antibiotics for the liver abscess, which was attributed to the presence of colonic polyps. It is postulated that colon cancer or adenoma-associated mucosal defects may facilitate bacterial infiltration into the portal circulation, thereby contributing to hepatic seeding and subsequent liver abscess formation.
Discussion: Pyogenic liver abscess associated with Klebsiella pneumoniae are commonly observed in individuals with concurrent diabetes mellitus and advanced age. In cases lacking evident hepatobiliary or intra-abdominal infections, which typically serve as primary sources of bacterial dissemination, the etiology of liver abscess often remains cryptogenic. However, it is essential to consider colonic adenoma or carcinoma as potential underlying causes in those with pyogenic liver abscess and warrants investigation.

Figure: Figure. Cross-sectional CT scan showing liver abscess (A) Descending colon polyp (B)
Disclosures:
Dongmin Shin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sameer Kandhi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Franklin Sosa indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nikhitha Mantri indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ali Ghazanfar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jasbir Makker indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Harish Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dongmin Shin, MD1, Sameer Kandhi, MD1, Franklin Sosa, MD1, Nikhitha Mantri, MD1, Ali Ghazanfar, MBBS2, Jasbir Makker, MD1, Harish Patel, MD1. P3873 - Association of Klebsiella pneumoniae Liver Abscess With Colonic Adenoma: A Case Report, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
