Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Esophagus
P3929 - Differences in Clinical Presentation and Treatment Response of Patients With Eosinophilic Esophagitis Complicated by Symptoms of Esophageal Food Impaction
Tuesday, October 29, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E

Has Audio

Walker D. Redd, MD
University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill School of Medicine
Chapel Hill, NC
Presenting Author(s)
Walker D. Redd, MD1, Trevor Barlowe, MD1, Sean S. LaFata, BS1, Tim S. Gee, BS1, Hannah L. Thel, BS1, Brenderia A. Cameron, MS1, Angela Z. Xue, MD, MPH1, Akshatha Kiran, MD, MPH2, Adolfo A. Ocampo, MD, MA1, Justin McCallen, MD1, Christopher J. Lee, MD1, Stephanie A. Borinsky, MD, MSCR1, Rayan N. Kaataki, MD1, Cary C. Cotton, MD, MPH1, Swathi Eluri, MD, MSCR3, Craig C. Reed, MD, MSCR1, Evan S.. Dellon, MD, MPH, FACG1
1University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill School of Medicine, Chapel Hill, NC; 2University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, NC; 3Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, FL
Introduction: Patients with eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) often have food impactions, but there are few data comparing patients with a history of food impaction symptoms to those who have not had a food impaction symptoms. To determine whether patients with EoE complicated by food impaction have differences in presentation or response to topical corticosteroid (tCS) treatment.
Methods: In this retrospective cohort, patients with a new diagnosis of EoE were divided into those who did and did not report food impaction symptoms. Demographics, clinical characteristics, procedural data, and histology results were extracted. For those treated with tCS, we assessed histological response defined as < 15 eos/hpf, with additional assessment of ≤6 and < 1 eos/hpf. Symptomatic and endoscopic response were also obtained. Patients with and without food impaction were compared using bivariate and multivariable analyses.
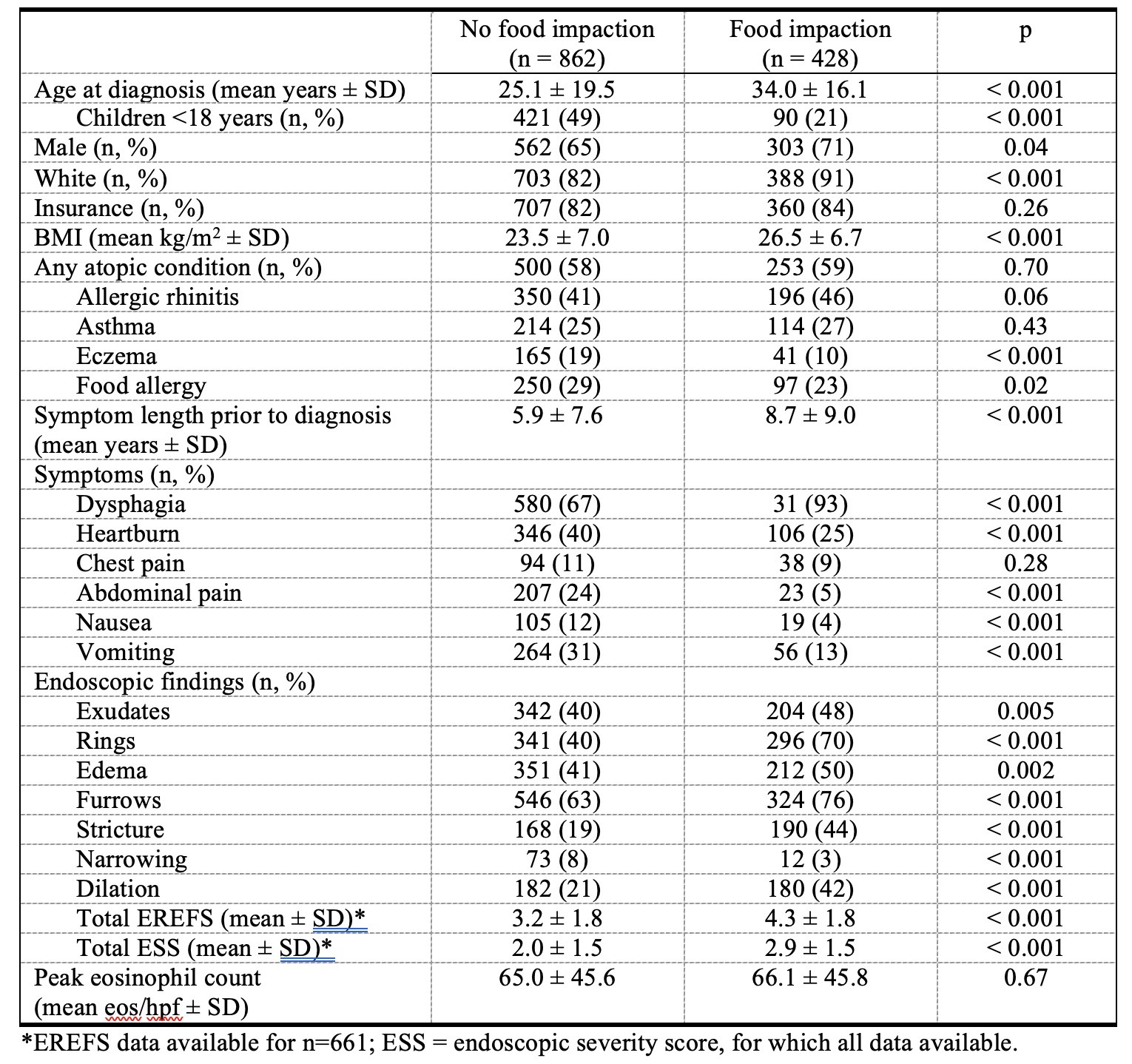
Results: Of 1,290 EoE patients with symptom data available, 428 (33%) had a food impaction history. Compared to those without food impaction symptoms, patients with impactions were older (34.0 vs 25.1 years; p< 0.001) and had a higher BMI (26.5 vs 23.5; p< 0.001), longer symptom duration (8.7 vs 5.9 years; p< 0.001), more dysphagia (93% vs 67%; p< 0.001), more dilation (42% vs 21%; p< 0.001), and more severe endoscopic findings (Table 1). Patients without food impaction reported more heartburn (40% vs 25%; p< 0.001), abdominal pain (24% vs 5%; p< 0.001), nausea (12% vs 4%; p< 0.001), and vomiting (31% vs 13%; p< 0.001). On multivariable analysis, higher BMI (OR 1.04 per 1 unit increase; CI 95%: 1.02-1.07), rings (OR 2.16; CI 95%: 1.69-2.91), and dilation (OR 1.84; CI 95%: 1.36-2.48) were associated with prior food impaction whereas heartburn (OR 0.45; CI 95%: 0.33-0.61), abdominal pain (OR 0.27; CI 95%: 0.16-0.45), and vomiting (OR 0.59; CI 95%: 0.41-0.87) were associated with not having prior food impaction. Symptomatic and tCS treatment response was similar regardless of food impaction history (Table 2). However, after treatment, patients with food impaction symptoms were more likely to have rings (60% vs 33%; p< 0.001), strictures (48% vs 21%; p< 0.001), and dilation (45% vs 21%; p< 0.001).
Discussion: Patients with EoE complicated by food impaction symptoms have more fibrostenotic features and more often require dilation compared to those without food impaction. The larger burden of fibrostenosis persists after tCS therapy despite similar histologic response.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Walker D. Redd, MD1, Trevor Barlowe, MD1, Sean S. LaFata, BS1, Tim S. Gee, BS1, Hannah L. Thel, BS1, Brenderia A. Cameron, MS1, Angela Z. Xue, MD, MPH1, Akshatha Kiran, MD, MPH2, Adolfo A. Ocampo, MD, MA1, Justin McCallen, MD1, Christopher J. Lee, MD1, Stephanie A. Borinsky, MD, MSCR1, Rayan N. Kaataki, MD1, Cary C. Cotton, MD, MPH1, Swathi Eluri, MD, MSCR3, Craig C. Reed, MD, MSCR1, Evan S.. Dellon, MD, MPH, FACG1. P3929 - Differences in Clinical Presentation and Treatment Response of Patients With Eosinophilic Esophagitis Complicated by Symptoms of Esophageal Food Impaction, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill School of Medicine, Chapel Hill, NC; 2University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, NC; 3Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, FL
Introduction: Patients with eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) often have food impactions, but there are few data comparing patients with a history of food impaction symptoms to those who have not had a food impaction symptoms. To determine whether patients with EoE complicated by food impaction have differences in presentation or response to topical corticosteroid (tCS) treatment.
Methods: In this retrospective cohort, patients with a new diagnosis of EoE were divided into those who did and did not report food impaction symptoms. Demographics, clinical characteristics, procedural data, and histology results were extracted. For those treated with tCS, we assessed histological response defined as < 15 eos/hpf, with additional assessment of ≤6 and < 1 eos/hpf. Symptomatic and endoscopic response were also obtained. Patients with and without food impaction were compared using bivariate and multivariable analyses.
Results: Of 1,290 EoE patients with symptom data available, 428 (33%) had a food impaction history. Compared to those without food impaction symptoms, patients with impactions were older (34.0 vs 25.1 years; p< 0.001) and had a higher BMI (26.5 vs 23.5; p< 0.001), longer symptom duration (8.7 vs 5.9 years; p< 0.001), more dysphagia (93% vs 67%; p< 0.001), more dilation (42% vs 21%; p< 0.001), and more severe endoscopic findings (Table 1). Patients without food impaction reported more heartburn (40% vs 25%; p< 0.001), abdominal pain (24% vs 5%; p< 0.001), nausea (12% vs 4%; p< 0.001), and vomiting (31% vs 13%; p< 0.001). On multivariable analysis, higher BMI (OR 1.04 per 1 unit increase; CI 95%: 1.02-1.07), rings (OR 2.16; CI 95%: 1.69-2.91), and dilation (OR 1.84; CI 95%: 1.36-2.48) were associated with prior food impaction whereas heartburn (OR 0.45; CI 95%: 0.33-0.61), abdominal pain (OR 0.27; CI 95%: 0.16-0.45), and vomiting (OR 0.59; CI 95%: 0.41-0.87) were associated with not having prior food impaction. Symptomatic and tCS treatment response was similar regardless of food impaction history (Table 2). However, after treatment, patients with food impaction symptoms were more likely to have rings (60% vs 33%; p< 0.001), strictures (48% vs 21%; p< 0.001), and dilation (45% vs 21%; p< 0.001).
Discussion: Patients with EoE complicated by food impaction symptoms have more fibrostenotic features and more often require dilation compared to those without food impaction. The larger burden of fibrostenosis persists after tCS therapy despite similar histologic response.

Figure: Table 1: Baseline characteristics of EoE patients without and with food impaction
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Walker Redd indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Trevor Barlowe indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sean LaFata indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tim Gee indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hannah Thel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Brenderia Cameron indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Angela Xue indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Akshatha Kiran indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Adolfo Ocampo indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Justin McCallen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Christopher Lee indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Stephanie Borinsky indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rayan Kaataki indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Cary Cotton: Pentax – Grant/Research Support.
Swathi Eluri indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Craig Reed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Evan Dellon: Abbott – Consultant. AbbVie – Consultant. Adare/Ellodi – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Aimmune – Consultant. Akesobio – Consultant. Alfasigma – Consultant. ALK – Consultant. Allakos – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Amgen – Consultant. Aqilion – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Arena/Pfizer – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Aslan – Consultant. AstraZeneca – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Avir – Consultant. Biorasi – Consultant. Calypso – Consultant. Celgene/Receptos/BMS – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Celldex – Consultant. Dr. Falk Pharma – Consultant. Eli Lilly – Consultant. EsoCap – Consultant. Eupraxia – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Ferring – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. GlaxoSmithKline – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Gossamer Bio – Consultant. Holoclara – Consultant. Holoclara – Grant/Research Support. Invea – Consultant. Invea – Grant/Research Support. Knightpoint – Consultant. Landos – Consultant. LucidDx – Consultant. Meritage – Grant/Research Support. Miraca – Grant/Research Support. Morphic – Consultant. Nexstone Immunology/Uniquity – Consultant. Nutricia – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Parexel/Calyx – Consultant. Phathom – Consultant. Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc. – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Revolo – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Robarts/Alimentiv – Consultant. Salix – Consultant. Sanofi – Consultant. Shire/Takeda – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Target RWE – Consultant. Upstream Bio – Consultant.
Walker D. Redd, MD1, Trevor Barlowe, MD1, Sean S. LaFata, BS1, Tim S. Gee, BS1, Hannah L. Thel, BS1, Brenderia A. Cameron, MS1, Angela Z. Xue, MD, MPH1, Akshatha Kiran, MD, MPH2, Adolfo A. Ocampo, MD, MA1, Justin McCallen, MD1, Christopher J. Lee, MD1, Stephanie A. Borinsky, MD, MSCR1, Rayan N. Kaataki, MD1, Cary C. Cotton, MD, MPH1, Swathi Eluri, MD, MSCR3, Craig C. Reed, MD, MSCR1, Evan S.. Dellon, MD, MPH, FACG1. P3929 - Differences in Clinical Presentation and Treatment Response of Patients With Eosinophilic Esophagitis Complicated by Symptoms of Esophageal Food Impaction, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
