Monday Poster Session
Category: Small Intestine
P3222 - Duodenal Ischemia From Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hematuria
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio
- SZ
Suha Zawawi, MD
Valley Hospital Medical Center
Las Vegas, NV
Presenting Author(s)
Suha Zawawi, MD, Scott Diamond, DO, Vishvinder Sharma, MD
Valley Hospital Medical Center, Las Vegas, NV
Introduction: Paroxysmal nocturnal hematuria (PNH) is an acquired defect in a red blood cell membrane protein protective complement mediated damage. Venous thromboemboli form from chronic intravascular hemolysis. The resultant free hemoglobin causes nitric oxide depletion, endothelial dysfunction and platelet activation creating microthrombi. Decreased nitric oxide promotes systemic vasoconstriction further impairing blood flow causing further ischemia. PNH can affect the entire GI tract with documented cases affecting the colon, stomach, pancreas and hepatic veins. We present a patient with PNH as the underlying etiology of endoscopic confirmed duodenal ischemia.
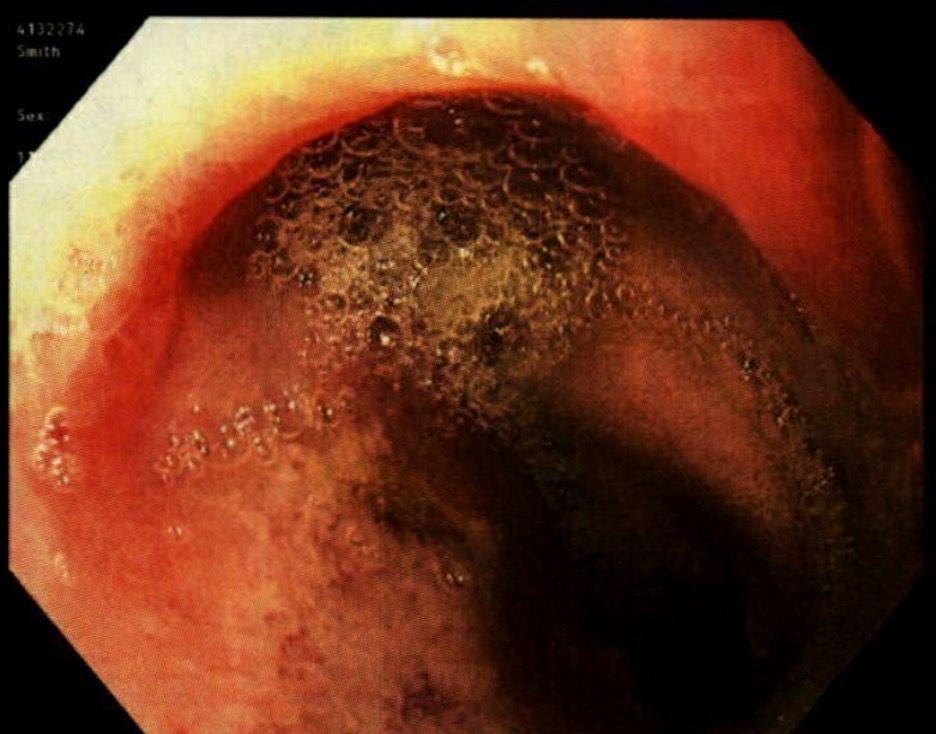
Case Description/Methods: A 20-year-old male with cytometry confirmed PNH and secondary aplastic anemia on bone marrow aspiration was admitted with generalized abdominal pain and hematuria. CT angiography showed thickening extending from the distal stomach to the mid jejunum with no large vessel occlusion. EGD showed edema with ulcerations of the duodenal bulb through D2 concerning for ischemia. Biopsy confirmed active duodenitis. Eculizumab and therapeutic heparin were started with symptom resolution.
Discussion: Venous thrombi, more commonly than arterial thrombi, occur in 40% of patients with PNH. Typical GI manifestations include esophageal dysphagia or unexplained abdominal pain from ischemia. Suspicion for PNH should be raised in the presence of hemoglobinuria, Coombs negative intravascular hemolysis, aplastic anemia and unexplained thrombi, especially in atypical locations such as the cavernous sinus, mesenteric and hepatic veins. PNH can be diagnosed by identifying lacking GPI-anchored proteins on flow cytometry.
Eculizumab is a monoclonal antibody which blocks the activation of the terminal compliment system at C5 thus preventing hemolysis in PNH. Treatment is indicated in patients with evidence hemolysis, thrombosis or cytopenias. Eculizumab may increase the risk infections from encapsulated organisms therefore vaccination is recommended prior to use.
PNH should be considered in young patients with hemolytic anemia coupled with evidence of GI ischemia absent the typical risk factors, especially if the affected organs are in an atypical vascular pattern. Prompt recognition and appropriate therapy with Eculizumab can prevent more serious complications of ischemia including end organ failure or perforation.
Disclosures:
Suha Zawawi, MD, Scott Diamond, DO, Vishvinder Sharma, MD. P3222 - Duodenal Ischemia From Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hematuria, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
Valley Hospital Medical Center, Las Vegas, NV
Introduction: Paroxysmal nocturnal hematuria (PNH) is an acquired defect in a red blood cell membrane protein protective complement mediated damage. Venous thromboemboli form from chronic intravascular hemolysis. The resultant free hemoglobin causes nitric oxide depletion, endothelial dysfunction and platelet activation creating microthrombi. Decreased nitric oxide promotes systemic vasoconstriction further impairing blood flow causing further ischemia. PNH can affect the entire GI tract with documented cases affecting the colon, stomach, pancreas and hepatic veins. We present a patient with PNH as the underlying etiology of endoscopic confirmed duodenal ischemia.
Case Description/Methods: A 20-year-old male with cytometry confirmed PNH and secondary aplastic anemia on bone marrow aspiration was admitted with generalized abdominal pain and hematuria. CT angiography showed thickening extending from the distal stomach to the mid jejunum with no large vessel occlusion. EGD showed edema with ulcerations of the duodenal bulb through D2 concerning for ischemia. Biopsy confirmed active duodenitis. Eculizumab and therapeutic heparin were started with symptom resolution.
Discussion: Venous thrombi, more commonly than arterial thrombi, occur in 40% of patients with PNH. Typical GI manifestations include esophageal dysphagia or unexplained abdominal pain from ischemia. Suspicion for PNH should be raised in the presence of hemoglobinuria, Coombs negative intravascular hemolysis, aplastic anemia and unexplained thrombi, especially in atypical locations such as the cavernous sinus, mesenteric and hepatic veins. PNH can be diagnosed by identifying lacking GPI-anchored proteins on flow cytometry.
Eculizumab is a monoclonal antibody which blocks the activation of the terminal compliment system at C5 thus preventing hemolysis in PNH. Treatment is indicated in patients with evidence hemolysis, thrombosis or cytopenias. Eculizumab may increase the risk infections from encapsulated organisms therefore vaccination is recommended prior to use.
PNH should be considered in young patients with hemolytic anemia coupled with evidence of GI ischemia absent the typical risk factors, especially if the affected organs are in an atypical vascular pattern. Prompt recognition and appropriate therapy with Eculizumab can prevent more serious complications of ischemia including end organ failure or perforation.

Figure: EGD showing ischemic duodenitis with edema and ulcerations
Disclosures:
Suha Zawawi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Scott Diamond indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vishvinder Sharma indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Suha Zawawi, MD, Scott Diamond, DO, Vishvinder Sharma, MD. P3222 - Duodenal Ischemia From Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hematuria, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
