Monday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P2936 - Fibroblast Growth Factor Analogues in Metabolic Dysfunction Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: A Network Meta-Analysis
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio
- ME
Mohamed Elnaggar, MD
Hartford HealthCare
Hartford, CT
Presenting Author(s)
Mohamed Elnaggar, MD1, Muhammad Imran, MBBS2, Islam Mohamed, MD3, Mohamed Abuelazm, MD4, Qasi Najah, MBBCh5, Abdelrahman Mahmoud, MBBCh6, Ahmed Mazen Amin, MBBCh7, Hazem Rezq, MBBCh8, Ubaid Khan, MD9, Basel Abdelazeem, MD10, Nikki Duong, MD11
1Hartford HealthCare, Hartford, CT; 2University College of Medicine and Dentistry, The University of Lahore, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 3University of Missouri - Kansas City School of Medicine, Kansas City, MO; 4Tanta University, Tanta, Al Gharbiyah, Egypt; 5Elmergib University, Alkhums, Al Marqab, Libya; 6Minia University, Minya, Al Minya, Egypt; 7Mansoura University, Mansoura, Ad Daqahliyah, Egypt; 8Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Ad Daqahliyah, Egypt; 9University of Maryland, Baltimore, MD; 10West Virginia University, Morgantown, WV; 11Stanford University, Stanford, CA
Introduction: Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) agonists have a promising role in metabolic dysfunction associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD). This study aims to evaluate the efficacy and safety of FGF agonists in patients with MASLD, aiming to identify the optimal regimen
Methods: Five databases were searched systemically through a search strategy to identify the relevant randomized controlled trials (RCTs), and Covidence was used for screening of eligible articles. The network meta-analysis was performed using the Netmeta package in R software and all the concerned outcomes were synthesized and presented as risk ratio (RR) or mean difference (MD) with 95% confidence interval (CI).
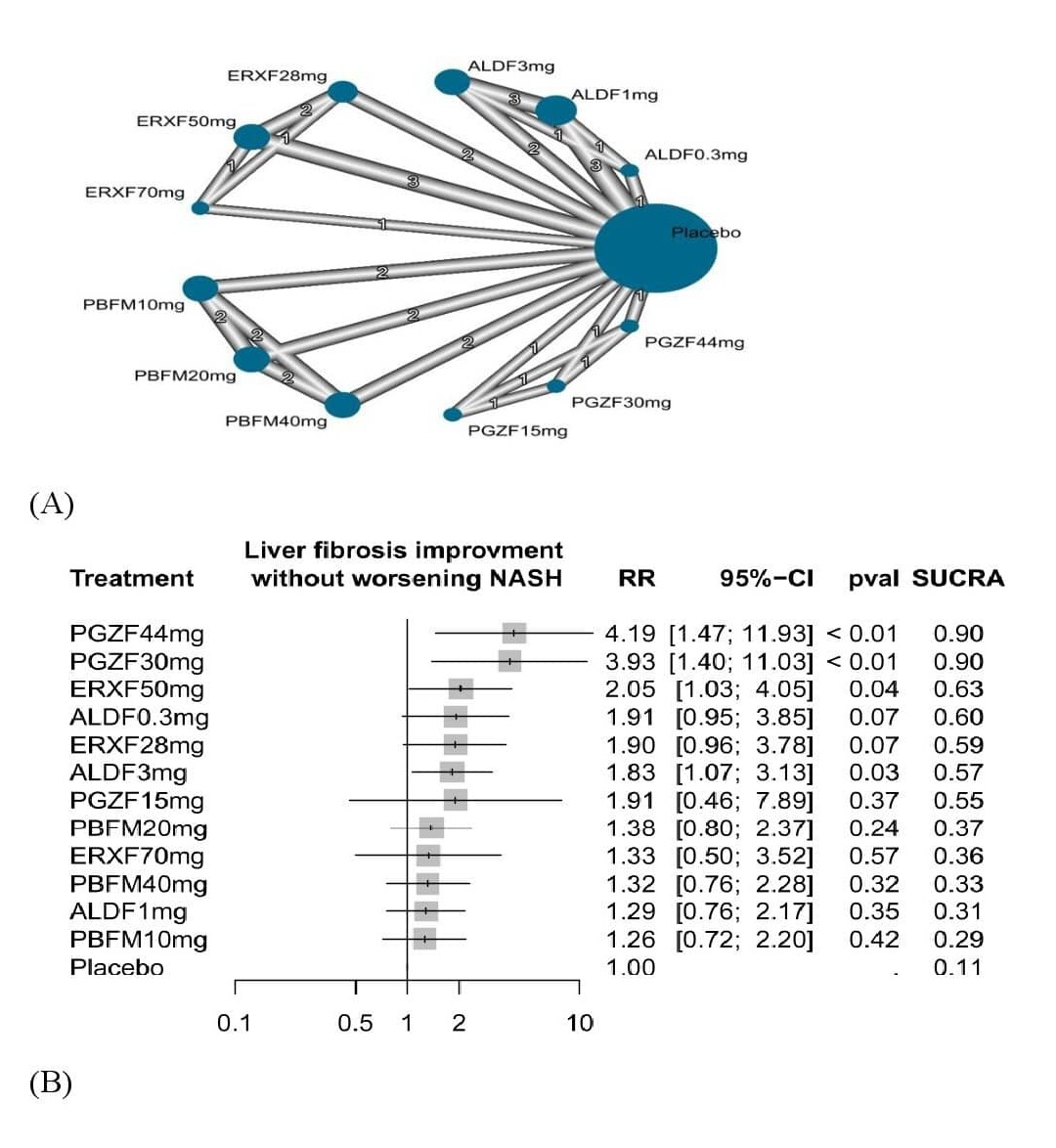
Results: Twelve RCTs comprising 1,420 patients with MASLD were included, involving four FGF agonists: efruxifermin, aldafermin, pegbelfermin, and pegozafermin at various doses. Most significant mean reduction in hepatic fat fraction (HFF) [MD = -67.98, 95% CI [-102.12; -33.84], P< 0.01] and reduction in HFF >30% [RR=4.68, 95% CI [2.57; 7.97], P< 0.01] were observed with efruxifermin at 70 mg, 50 mg, and 28 mg compared to placebo. Pegozafermin at 44 mg (RR=4.19, 95% CI [1.47; 11.93], P< 0.01) and 30 mg (RR=3.93, 95% CI [1.40; 11.03], P< 0.01) had the most significant improvement in liver fibrosis equal to or >1 stage without MASH worsening followed by efruxifermin at 50 mg (P=0.04). Improvement in other non-invasive, histological and metabolic aspects of MASLD were observed with various FGF regimens.
Discussion: FGF agonists at various doses showed significant improvements in HFF, steatohepatitis, fibrosis and metabolic parameters with the tolerable safety profile indicating their potential in managing patients with MASLD.
Disclosures:
Mohamed Elnaggar, MD1, Muhammad Imran, MBBS2, Islam Mohamed, MD3, Mohamed Abuelazm, MD4, Qasi Najah, MBBCh5, Abdelrahman Mahmoud, MBBCh6, Ahmed Mazen Amin, MBBCh7, Hazem Rezq, MBBCh8, Ubaid Khan, MD9, Basel Abdelazeem, MD10, Nikki Duong, MD11. P2936 - Fibroblast Growth Factor Analogues in Metabolic Dysfunction Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: A Network Meta-Analysis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Hartford HealthCare, Hartford, CT; 2University College of Medicine and Dentistry, The University of Lahore, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 3University of Missouri - Kansas City School of Medicine, Kansas City, MO; 4Tanta University, Tanta, Al Gharbiyah, Egypt; 5Elmergib University, Alkhums, Al Marqab, Libya; 6Minia University, Minya, Al Minya, Egypt; 7Mansoura University, Mansoura, Ad Daqahliyah, Egypt; 8Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Ad Daqahliyah, Egypt; 9University of Maryland, Baltimore, MD; 10West Virginia University, Morgantown, WV; 11Stanford University, Stanford, CA
Introduction: Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) agonists have a promising role in metabolic dysfunction associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD). This study aims to evaluate the efficacy and safety of FGF agonists in patients with MASLD, aiming to identify the optimal regimen
Methods: Five databases were searched systemically through a search strategy to identify the relevant randomized controlled trials (RCTs), and Covidence was used for screening of eligible articles. The network meta-analysis was performed using the Netmeta package in R software and all the concerned outcomes were synthesized and presented as risk ratio (RR) or mean difference (MD) with 95% confidence interval (CI).
Results: Twelve RCTs comprising 1,420 patients with MASLD were included, involving four FGF agonists: efruxifermin, aldafermin, pegbelfermin, and pegozafermin at various doses. Most significant mean reduction in hepatic fat fraction (HFF) [MD = -67.98, 95% CI [-102.12; -33.84], P< 0.01] and reduction in HFF >30% [RR=4.68, 95% CI [2.57; 7.97], P< 0.01] were observed with efruxifermin at 70 mg, 50 mg, and 28 mg compared to placebo. Pegozafermin at 44 mg (RR=4.19, 95% CI [1.47; 11.93], P< 0.01) and 30 mg (RR=3.93, 95% CI [1.40; 11.03], P< 0.01) had the most significant improvement in liver fibrosis equal to or >1 stage without MASH worsening followed by efruxifermin at 50 mg (P=0.04). Improvement in other non-invasive, histological and metabolic aspects of MASLD were observed with various FGF regimens.
Discussion: FGF agonists at various doses showed significant improvements in HFF, steatohepatitis, fibrosis and metabolic parameters with the tolerable safety profile indicating their potential in managing patients with MASLD.

Figure: Liver fibrosis improvement without worsening NASH.
Disclosures:
Mohamed Elnaggar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Imran indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Islam Mohamed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohamed Abuelazm indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Qasi Najah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdelrahman Mahmoud indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmed Mazen Amin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hazem Rezq indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ubaid Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Basel Abdelazeem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nikki Duong indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohamed Elnaggar, MD1, Muhammad Imran, MBBS2, Islam Mohamed, MD3, Mohamed Abuelazm, MD4, Qasi Najah, MBBCh5, Abdelrahman Mahmoud, MBBCh6, Ahmed Mazen Amin, MBBCh7, Hazem Rezq, MBBCh8, Ubaid Khan, MD9, Basel Abdelazeem, MD10, Nikki Duong, MD11. P2936 - Fibroblast Growth Factor Analogues in Metabolic Dysfunction Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: A Network Meta-Analysis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
