Monday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P2731 - Coughs and Colitis: A Tale of Two Troubled Organs
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Micah Vander Griend, MPH
University of Kansas School of Medicine
Wichita, KS
Presenting Author(s)
Micah Vander Griend, MPH1, Marisa-Nicole Zayat, MD1, Diala Merheb, MD1, Mahmoud Mahdi, MD1, Estephan Zayat, MD2
1University of Kansas School of Medicine, Wichita, KS; 2Kansas Gastroenterology and Endoscopy, LLC, Wichita, KS
Introduction: Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a chronic inflammatory disease affecting the colon and rectum. However, this disease can also have diverse extraintestinal manifestations that can affect the skin, joints, biliary tract, eyes, and, rarely, the lungs.
Case Description/Methods: A 66-year-old female marathon runner and dental hygienist with a 50-year history of ulcerative pancolitis in deep remission on mesalamine presented with a chronic, non-productive cough. CT imaging revealed cylindrical and varicose bronchiectasis with airway thickening, mucus plugging, multifocal tree-in-bud nodularities, and diffuse gas trapping, compatible with interstitial lung disease (ILD). After extensive pulmonary workup, including a negative evaluation for reflux, she was diagnosed with ILD attributed to her long-standing UC. Consideration for infliximab was recommended. Symbicort, azithromycin, steroids, tobramycin, and hypertonic saline nasal spray were also initiated. Interestingly, it was noted that her cough improved after infliximab infusions, progressively worsening directly prior to her upcoming infusion.
Discussion: This case report highlights an interesting and uncommon extraintestinal manifestation of UC. It is postulated that since both the bowel and lungs develop from similar embryonic origins and that both tissues contain similar adhesion molecules for leukocyte migration, these disease processes may be linked.¹ Despite the rare occurrence of pulmonary complications experienced by those with UC, thorough investigation remains an important tool for gastroenterologists seeing patients with new-onset symptoms that may seem unrelated to their presenting disease.

Disclosures:
Micah Vander Griend, MPH1, Marisa-Nicole Zayat, MD1, Diala Merheb, MD1, Mahmoud Mahdi, MD1, Estephan Zayat, MD2. P2731 - Coughs and Colitis: A Tale of Two Troubled Organs, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of Kansas School of Medicine, Wichita, KS; 2Kansas Gastroenterology and Endoscopy, LLC, Wichita, KS
Introduction: Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a chronic inflammatory disease affecting the colon and rectum. However, this disease can also have diverse extraintestinal manifestations that can affect the skin, joints, biliary tract, eyes, and, rarely, the lungs.
Case Description/Methods: A 66-year-old female marathon runner and dental hygienist with a 50-year history of ulcerative pancolitis in deep remission on mesalamine presented with a chronic, non-productive cough. CT imaging revealed cylindrical and varicose bronchiectasis with airway thickening, mucus plugging, multifocal tree-in-bud nodularities, and diffuse gas trapping, compatible with interstitial lung disease (ILD). After extensive pulmonary workup, including a negative evaluation for reflux, she was diagnosed with ILD attributed to her long-standing UC. Consideration for infliximab was recommended. Symbicort, azithromycin, steroids, tobramycin, and hypertonic saline nasal spray were also initiated. Interestingly, it was noted that her cough improved after infliximab infusions, progressively worsening directly prior to her upcoming infusion.
Discussion: This case report highlights an interesting and uncommon extraintestinal manifestation of UC. It is postulated that since both the bowel and lungs develop from similar embryonic origins and that both tissues contain similar adhesion molecules for leukocyte migration, these disease processes may be linked.¹ Despite the rare occurrence of pulmonary complications experienced by those with UC, thorough investigation remains an important tool for gastroenterologists seeing patients with new-onset symptoms that may seem unrelated to their presenting disease.

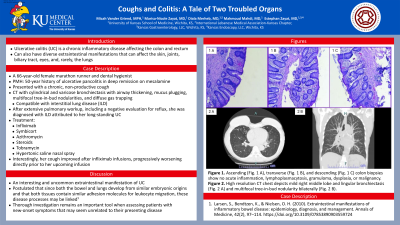
Figure: Figure 1. Ascending (Fig. 1 A), transverse (Fig. 1 B), and descending (Fig. 1 C) colon biopsies show no acute inflammation, lymphoplasmacytosis, gramuloma, dysplasia, or malignancy.
Figure 2. High resolution CT chest depicts mild right middle lobe and lingular bronchiectasis (Fig. 2 A) and multifocal tree-in-bud nodularity bilaterally (Fig. 2 B).
Figure 2. High resolution CT chest depicts mild right middle lobe and lingular bronchiectasis (Fig. 2 A) and multifocal tree-in-bud nodularity bilaterally (Fig. 2 B).
Disclosures:
Micah Vander Griend indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Marisa-Nicole Zayat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Diala Merheb indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mahmoud Mahdi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Estephan Zayat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Micah Vander Griend, MPH1, Marisa-Nicole Zayat, MD1, Diala Merheb, MD1, Mahmoud Mahdi, MD1, Estephan Zayat, MD2. P2731 - Coughs and Colitis: A Tale of Two Troubled Organs, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.

