Monday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P2640 - The National Burden of Inflammatory Bowel Disease in the United States from 1990 to 2021
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio
- OA
Omar Al Ta'ani, MD
Allegheny Health Network
Pittsburgh, PA
Presenting Author(s)
Omar Al Ta'ani, MD, Gursimran S. Kochhar, MD, FACG
Allegheny Health Network, Pittsburgh, PA
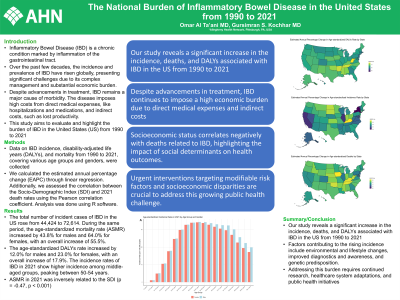
Introduction: Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) is a chronic condition marked by inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract. Over the past few decades, the incidence and prevalence of IBD have risen globally, presenting significant challenges due to its complex management and substantial economic burden. Despite advancements in treatment, IBD remains a major cause of morbidity. The disease imposes high costs from direct medical expenses, like hospitalizations and medications, and indirect costs, such as lost productivity. This study aims to evaluate the burden of IBD in the United States (US) from 1990 to 2021
Methods: Our study examines the burden of IBD in the US using data from the Global Burden of Disease database. Data on IBD incidence, disability-adjusted life years (DALYs), and mortality from 1990 to 2021, covering various age groups and genders, were collected. We calculated the estimated annual percentage change (EAPC) through linear regression. Additionally, we assessed the correlation between the Socio-Demographic Index (SDI) and 2021 death rates using the Pearson correlation coefficient. All analyses and data visualizations were performed using R programming version 4.3.3
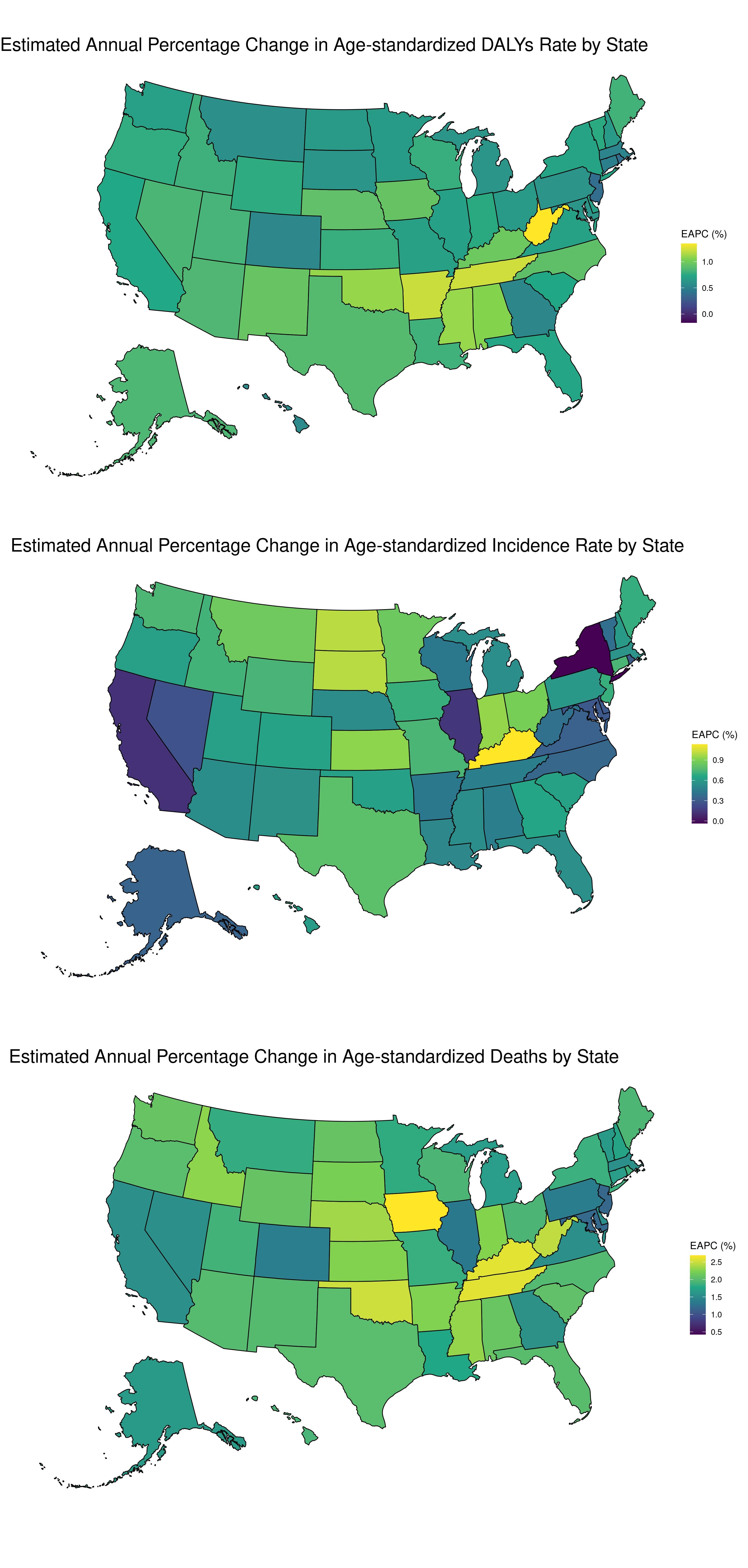
Results: From 1990 to 2021, the total number of incident cases of IBD in the US rose from 44,424 to 72,614. During the same period, the age-standardized mortality rate (ASMR) increased by 43.8% for males and 64.0% for females, with an overall increase of 55.5%. Additionally, the age-standardized DALYs rate increased showed an overall increase of 17.9%. The incidence rates of IBD in 2021 show higher incidence among middle-aged groups and the ASMR attributable to IBD continued to increase significantly with age. Disparities in EAPC between states exist; for instance, Kentucky had the highest EAPC of age-standardized incidence rates at 1.13% (0.91 - 1.35), while New York had the lowest EAPC at -0.06% (-0.19 - 0.12). Additionally, ASMR in 2021 was inversely related to the SDI (p = -0.47, p < 0.001)
Discussion: Our study reveals a significant increase in the incidence, deaths, and DALYs associated with IBD in the US from 1990 to 2021. Factors contributing to the rising incidence include environmental and lifestyle changes, as well as improved diagnostics and awareness. Despite advancements in treatment, IBD continues to impose a high economic burden due to direct medical expenses and indirect costs. Addressing this burden requires continued research, healthcare system adaptations, and public health initiatives
Disclosures:
Omar Al Ta'ani, MD, Gursimran S. Kochhar, MD, FACG. P2640 - The National Burden of Inflammatory Bowel Disease in the United States from 1990 to 2021, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
Allegheny Health Network, Pittsburgh, PA
Introduction: Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) is a chronic condition marked by inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract. Over the past few decades, the incidence and prevalence of IBD have risen globally, presenting significant challenges due to its complex management and substantial economic burden. Despite advancements in treatment, IBD remains a major cause of morbidity. The disease imposes high costs from direct medical expenses, like hospitalizations and medications, and indirect costs, such as lost productivity. This study aims to evaluate the burden of IBD in the United States (US) from 1990 to 2021
Methods: Our study examines the burden of IBD in the US using data from the Global Burden of Disease database. Data on IBD incidence, disability-adjusted life years (DALYs), and mortality from 1990 to 2021, covering various age groups and genders, were collected. We calculated the estimated annual percentage change (EAPC) through linear regression. Additionally, we assessed the correlation between the Socio-Demographic Index (SDI) and 2021 death rates using the Pearson correlation coefficient. All analyses and data visualizations were performed using R programming version 4.3.3
Results: From 1990 to 2021, the total number of incident cases of IBD in the US rose from 44,424 to 72,614. During the same period, the age-standardized mortality rate (ASMR) increased by 43.8% for males and 64.0% for females, with an overall increase of 55.5%. Additionally, the age-standardized DALYs rate increased showed an overall increase of 17.9%. The incidence rates of IBD in 2021 show higher incidence among middle-aged groups and the ASMR attributable to IBD continued to increase significantly with age. Disparities in EAPC between states exist; for instance, Kentucky had the highest EAPC of age-standardized incidence rates at 1.13% (0.91 - 1.35), while New York had the lowest EAPC at -0.06% (-0.19 - 0.12). Additionally, ASMR in 2021 was inversely related to the SDI (p = -0.47, p < 0.001)
Discussion: Our study reveals a significant increase in the incidence, deaths, and DALYs associated with IBD in the US from 1990 to 2021. Factors contributing to the rising incidence include environmental and lifestyle changes, as well as improved diagnostics and awareness. Despite advancements in treatment, IBD continues to impose a high economic burden due to direct medical expenses and indirect costs. Addressing this burden requires continued research, healthcare system adaptations, and public health initiatives

Figure: Estimated annual percentage change in age-standardized incidence, DALYs, and deaths rates from 1990 to 2021.
Disclosures:
Omar Al Ta'ani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Gursimran Kochhar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Omar Al Ta'ani, MD, Gursimran S. Kochhar, MD, FACG. P2640 - The National Burden of Inflammatory Bowel Disease in the United States from 1990 to 2021, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
