Monday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P2646 - Recombinant Zoster Vaccine Uptake in US Adults with Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio
- NS
Nikita Stempniewicz, MSc
GSK
Philadelphia, PA
Presenting Author(s)
Justin Gatwood, PhD, MPH1, Catherine McGuiness, MA, MSc2, Marie Yasuda, PharmD, MS2, Chi-Chang Chen, PhD, PharmD, MS2, Nikita Stempniewicz, MSc1
1GSK, Philadelphia, PA; 2IQVIA, Wayne, PA
Introduction: Adults with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) are at higher risk for herpes zoster (HZ) compared to the immunocompetent US population aged ≥ 50 years. To prevent HZ, two doses of recombinant zoster vaccine (RZV) are recommended for adults ≥ 19 years who are or will be immunodeficient or immunosuppressed because of disease or therapy. However, given the recency of the recommendation, it is unclear whether such guidance has led to changes in RZV uptake.
Methods: This retrospective cross-sectional analysis used IQVIA open-source medical and pharmacy claims (10/20/2021 to 06/30/2023) to describe RZV uptake among adults ≥ 19 years old with evidence (ICD-10 diagnostic codes) of Crohn’s disease (CD) or ulcerative colitis (UC). Patients were followed from October 20, 2021 (date of ACIP vote) through the earlier of HZ vaccination or end of the study period. Outcomes included RZV uptake proportion (i.e., at least 1 dose), series completion (2 doses), and dosing interval adherence (second dose within 6 months of the initial dose). RZV uptake was assessed descriptively, and Kaplan-Meier analyses estimated time to series completion. A generalized estimating equation, controlling for patient demographics, clinical characteristics, and social determinants of health, predicted the odds of RZV uptake across the IBD conditions.
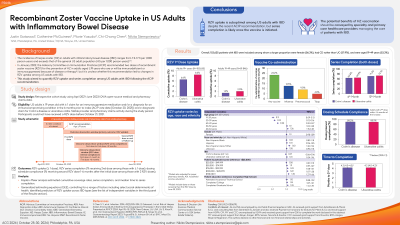
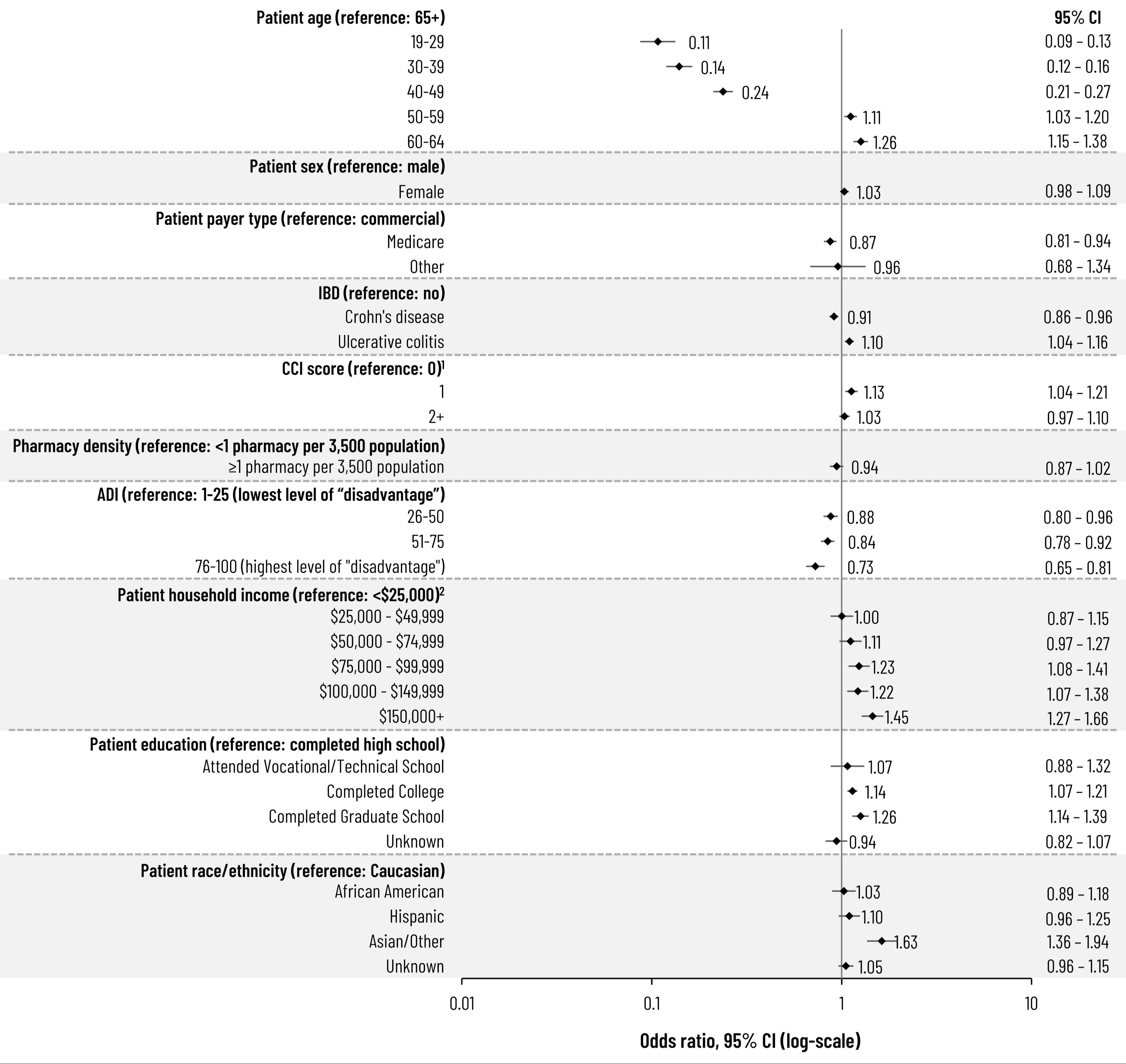
Results: A total of 153,635 patients were identified, among whom a larger proportion were female (56.3%), had CD rather than UC (57.9%), and were aged 19-49 years (53.3%). Overall RZV uptake was 6.6% and 8.5% for those with CD or UC, respectively, through June 2023; however, only 1.3% of CD patients and 2.0% of UC patients aged 19-49 years received at least 1 RZV dose. Series completion (2 doses) at 6-months was 63.8% for CD and 64.8% for UC, among which 89.2% and 88.5% complied with the recommended dosing schedule. Compared to patients with CD, patients with UC were more likely to receive RZV (odds ratio [OR]: 1.10; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.039-1.161) while, compared to adults >65 years, those < 50 years were less likely to have been vaccinated (Fig. 1).
Discussion: RZV uptake among adults with IBD is suboptimal despite the recent recommendation provided by ACIP leaving an ongoing unmet medical need in a population at high risk for HZ, particularly among those < 50 years.
Disclosures:
Justin Gatwood, PhD, MPH1, Catherine McGuiness, MA, MSc2, Marie Yasuda, PharmD, MS2, Chi-Chang Chen, PhD, PharmD, MS2, Nikita Stempniewicz, MSc1. P2646 - Recombinant Zoster Vaccine Uptake in US Adults with Inflammatory Bowel Disease, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1GSK, Philadelphia, PA; 2IQVIA, Wayne, PA
Introduction: Adults with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) are at higher risk for herpes zoster (HZ) compared to the immunocompetent US population aged ≥ 50 years. To prevent HZ, two doses of recombinant zoster vaccine (RZV) are recommended for adults ≥ 19 years who are or will be immunodeficient or immunosuppressed because of disease or therapy. However, given the recency of the recommendation, it is unclear whether such guidance has led to changes in RZV uptake.
Methods: This retrospective cross-sectional analysis used IQVIA open-source medical and pharmacy claims (10/20/2021 to 06/30/2023) to describe RZV uptake among adults ≥ 19 years old with evidence (ICD-10 diagnostic codes) of Crohn’s disease (CD) or ulcerative colitis (UC). Patients were followed from October 20, 2021 (date of ACIP vote) through the earlier of HZ vaccination or end of the study period. Outcomes included RZV uptake proportion (i.e., at least 1 dose), series completion (2 doses), and dosing interval adherence (second dose within 6 months of the initial dose). RZV uptake was assessed descriptively, and Kaplan-Meier analyses estimated time to series completion. A generalized estimating equation, controlling for patient demographics, clinical characteristics, and social determinants of health, predicted the odds of RZV uptake across the IBD conditions.
Results: A total of 153,635 patients were identified, among whom a larger proportion were female (56.3%), had CD rather than UC (57.9%), and were aged 19-49 years (53.3%). Overall RZV uptake was 6.6% and 8.5% for those with CD or UC, respectively, through June 2023; however, only 1.3% of CD patients and 2.0% of UC patients aged 19-49 years received at least 1 RZV dose. Series completion (2 doses) at 6-months was 63.8% for CD and 64.8% for UC, among which 89.2% and 88.5% complied with the recommended dosing schedule. Compared to patients with CD, patients with UC were more likely to receive RZV (odds ratio [OR]: 1.10; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.039-1.161) while, compared to adults >65 years, those < 50 years were less likely to have been vaccinated (Fig. 1).
Discussion: RZV uptake among adults with IBD is suboptimal despite the recent recommendation provided by ACIP leaving an ongoing unmet medical need in a population at high risk for HZ, particularly among those < 50 years.

Figure: Figure 1. Adjusted Risk of Herpes Zoster among US Adults with Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Notes:
1. Charlson Comorbidity Index, D-M adaptation, excluding Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis.
2. The ‘missing/unknown’ category has been omitted given its value is close to 0.
ADI, area-deprivation index; CCI, Charlson comorbidity index; CI, confidence interval; IBD, inflammatory bowel disease.
Notes:
1. Charlson Comorbidity Index, D-M adaptation, excluding Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis.
2. The ‘missing/unknown’ category has been omitted given its value is close to 0.
ADI, area-deprivation index; CCI, Charlson comorbidity index; CI, confidence interval; IBD, inflammatory bowel disease.
Disclosures:
Justin Gatwood: AstraZeneca – Grant/Research Support. Genentech – Consultant. GSK – Employee, Stock Options. Janssen – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Merck & Co. – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Grant/Research Support.
Catherine McGuiness: GSK – Consultant. IQVIA – Employee.
Marie Yasuda: Amgen – Grant/Research Support. Bayer – Grant/Research Support. BMS – Grant/Research Support. IQVIA – Employee. Novartis – Grant/Research Support. Sandoz – Grant/Research Support. Servier – Grant/Research Support.
Chi-Chang Chen: Amgen – Grant/Research Support. Bayer – Grant/Research Support. GSK – Grant/Research Support. IQVIA – Employee. Novartis – Grant/Research Support. Otsuka – Grant/Research Support. Servier – Grant/Research Support.
Nikita Stempniewicz: GSK – Employee, Stock Options.
Justin Gatwood, PhD, MPH1, Catherine McGuiness, MA, MSc2, Marie Yasuda, PharmD, MS2, Chi-Chang Chen, PhD, PharmD, MS2, Nikita Stempniewicz, MSc1. P2646 - Recombinant Zoster Vaccine Uptake in US Adults with Inflammatory Bowel Disease, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.

