Monday Poster Session
Category: GI Bleeding
P2520 - A Rare Case of Plasmablastic Lymphoma in a Patient Presenting With Gastrointestinal Bleeding
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Ruhi Vasavada-Patel, MD
Tampa General Hospital / University of South Florida
Tampa, FL
Presenting Author(s)
Ruhi Vasavada-Patel, MD, Camille S. Thélin, MD, MSc
Tampa General Hospital / University of South Florida, Tampa, FL
Introduction: Plasmablastic lymphoma (PBL) is a rare and aggressive form of B cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma that confers a poor prognosis. It is typically found in patients diagnosed with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and most often identified within the oropharyngeal cavity. Here, we discuss a case of PBL in a patient with previously diagnosed IgA kappa myeloma, who presented with gastrointestinal bleeding.
Case Description/Methods: 87-year-old male with IgA kappa myeloma, with no high-risk features, presented with a three-day history of melena. His hemoglobin on admission was 6 g/dl. Patient underwent endoscopy, which showed a 12 mm duodenal lesion with heaped up borders and centralized hematin without a visible vessel or ulcer bed. Patient also underwent colonoscopy, which showed a submucosal lesion 45 cm from the anal verge. Bite-on-bite biopsies were taken of this lesion. Video capsule endoscopy was negative. Computerized tomography scan revealed metastatic disease with the kidneys, bladder, pancreas, and lungs. Pathology of both lesions revealed neoplasm with plasma cell differentiation and plasmablastic morphology. Discussions with Oncology revealed final diagnosis of plasmablastic lymphoma. Patient was offered treatment with experimental regimen. However, due to his poor overall prognosis, patient elected to pursue hospice and comfort measures.
Discussion: This case highlights a rare malignancy that was diagnosed at an uncommon site in a patient without HIV. The incidence of PBL is unknown. Data demonstrates a 2% incidence of PBL in patients with AIDS-related lymphomas, with an even lower incidence in patients without HIV or AIDS. Another US study demonstrated that 69% of PBL cases were HIV-positive. Our patient was not HIV positive. Additionally, the most common site of PBL at the time of diagnosis is the oropharyngeal cavity. Our patient was diagnosed with PBL in the duodenum and colon after presenting with a gastrointestinal bleed. Unfortunately, prognosis of a patient diagnosed with metastatic PBL is poor with no established standard of care. One regimen includes cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin hydrochloride, vincristine sulfate, and prednisone but it has failed to produce durable remission. Smaller studies have evaluated daratumumab with etoposide, prednisone, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, and doxorubicin with modest survival benefit.
Disclosures:
Ruhi Vasavada-Patel, MD, Camille S. Thélin, MD, MSc. P2520 - A Rare Case of Plasmablastic Lymphoma in a Patient Presenting With Gastrointestinal Bleeding, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
Tampa General Hospital / University of South Florida, Tampa, FL
Introduction: Plasmablastic lymphoma (PBL) is a rare and aggressive form of B cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma that confers a poor prognosis. It is typically found in patients diagnosed with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and most often identified within the oropharyngeal cavity. Here, we discuss a case of PBL in a patient with previously diagnosed IgA kappa myeloma, who presented with gastrointestinal bleeding.
Case Description/Methods: 87-year-old male with IgA kappa myeloma, with no high-risk features, presented with a three-day history of melena. His hemoglobin on admission was 6 g/dl. Patient underwent endoscopy, which showed a 12 mm duodenal lesion with heaped up borders and centralized hematin without a visible vessel or ulcer bed. Patient also underwent colonoscopy, which showed a submucosal lesion 45 cm from the anal verge. Bite-on-bite biopsies were taken of this lesion. Video capsule endoscopy was negative. Computerized tomography scan revealed metastatic disease with the kidneys, bladder, pancreas, and lungs. Pathology of both lesions revealed neoplasm with plasma cell differentiation and plasmablastic morphology. Discussions with Oncology revealed final diagnosis of plasmablastic lymphoma. Patient was offered treatment with experimental regimen. However, due to his poor overall prognosis, patient elected to pursue hospice and comfort measures.
Discussion: This case highlights a rare malignancy that was diagnosed at an uncommon site in a patient without HIV. The incidence of PBL is unknown. Data demonstrates a 2% incidence of PBL

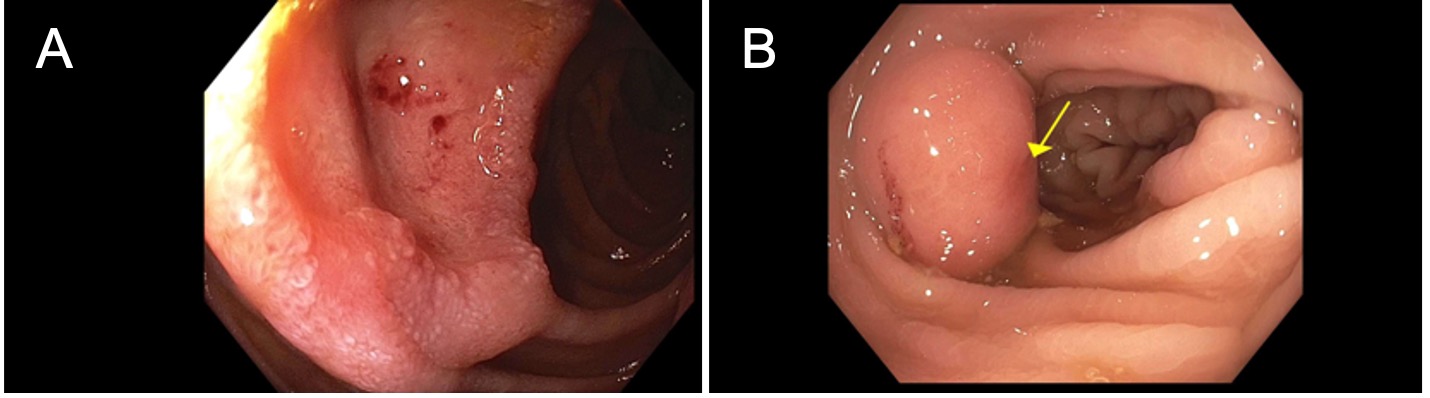
Figure: Figure 1: A) 12 mm ulcer with central hematin with biopsies consistent with plasmablastic lymphoma found on duodenal sweep B) submucosal lesion 45 cm from anal verge with biopsies consistent with plasmablastic lymphoma
Disclosures:
Ruhi Vasavada-Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Camille Thélin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ruhi Vasavada-Patel, MD, Camille S. Thélin, MD, MSc. P2520 - A Rare Case of Plasmablastic Lymphoma in a Patient Presenting With Gastrointestinal Bleeding, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.

