Monday Poster Session
Category: GI Bleeding
P2446 - Evaluating Gastrointestinal Bleeding Risks: A Meta-Analysis Comparing Direct Oral Anticoagulants and Warfarin in Older Adult Patients With Atrial Fibrillation
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Ahmad Zain, MD
UChealth Parkview Medical Center
Pueblo, CO
Presenting Author(s)
Hamza Naeem, MD1, Umar Abdul Rehman Khalid, MD1, Ahmad Zain, MD2, Mohammad Maheer Mubashir, 1, Abdul Mueed Bangash, MBBS3, Usama Qamar, MD1, Masood Azhar, MD1, Rida Ayesha Rafique, MD1, Ijlal Akbar Ali, MD4, Muhammad Umair, MD1, Muhammad Shehryar, MD1, Muhammad Bilal Shahid, MBBS1, Usama Ali, MD1, Muhammad Abdullah Javed, MD1
1King Edward Medical University, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 2UChealth Parkview Medical Center, Pueblo, CO; 3Khyber Teaching Hospital, Peshawar, North-West Frontier, Pakistan; 4University of Oklahoma College of Medicine, Oklahoma City, OK
Introduction: The recently published randomized trial Frail-AF raised ambiguity regarding the safety of using direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) over warfarin in older adult patients (≥65) with atrial fibrillation (AF). This meta-analysis aims to evaluate gastrointestinal bleeding, major bleeding, or all-cause mortality in these patients.
Methods: We searched Google Scholar, Scopus, Embase, and Pubmed from inception to June 2024 for relevant publications reporting gastrointestinal bleeding, major bleeding (any bleeding in a critical area or organ), or all-cause mortality. Only studies presenting the clinical outcomes data on older adult patients (≥65) with AF, with patients on either DOACs (Epixaban, Rivaroxaban, or Dabigatran), or warfarin, double-arm studies (randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and retrospective Studies), and those with outcomes given in the form of number-of-events were included. Studies without data on AF, with patient age less than 65 years, or single-arm studies (no comparison group) were excluded. Revman 5.4 was used to analyze the data.
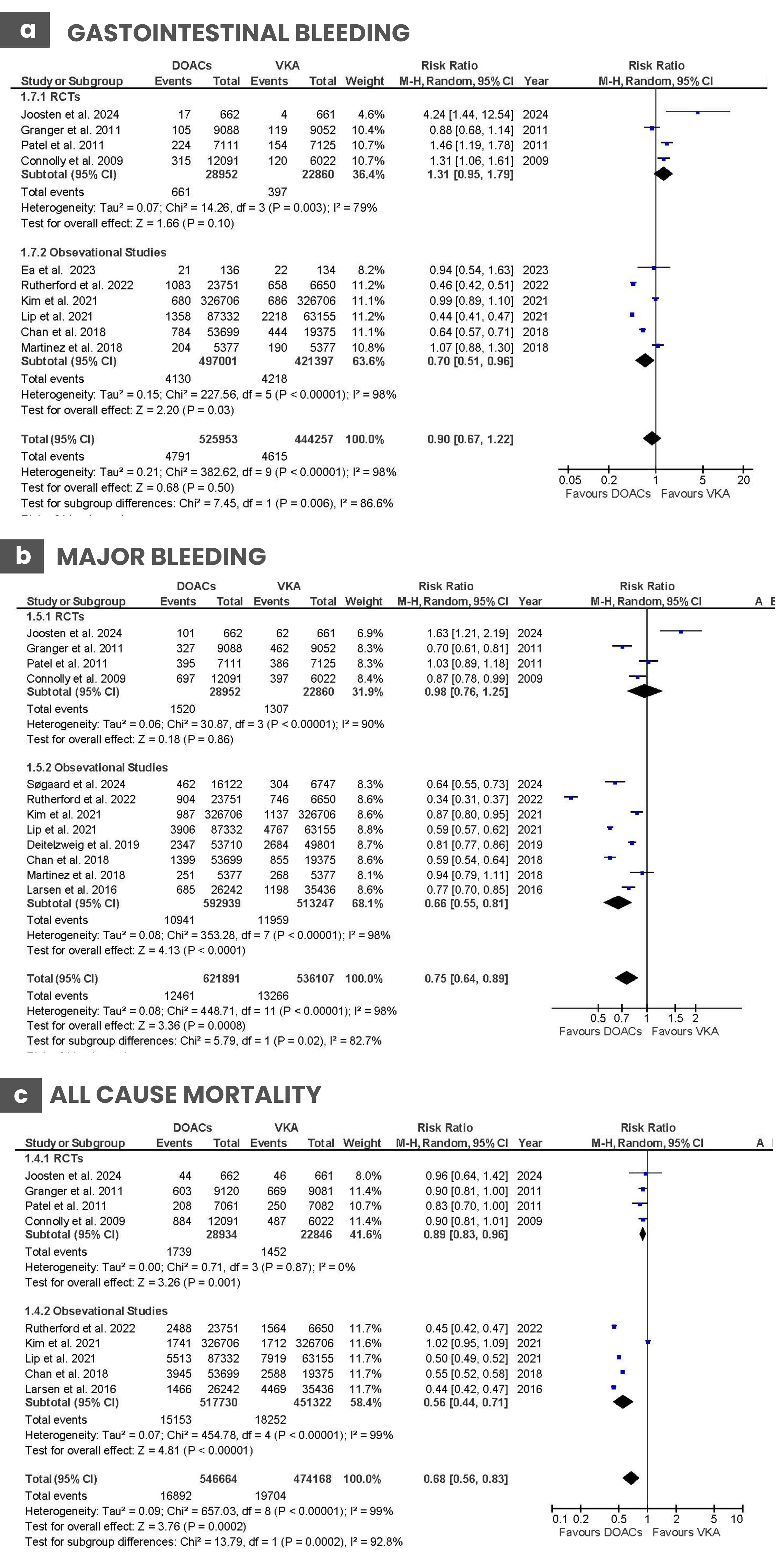
Results: We included 14 studies with a total of 589,262 patients. The pooled risk ratios (RR) with 95% confidence interval for gastrointestinal bleeding was 0.90 [0.67, 1.22], (P = 0.50), for major bleeding, it was 0.75 [0.64, 0.89], (P = 0.0008), for all-cause mortality = 0.68 [0.56, 0.83], (P = 0.0002). DOACs did not significantly reduce the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding compared to warfarin. DOACs demonstrated a statistically significant reduction in major bleeding and all-cause mortality compared to the use of warfarin. In the subgroup sensitivity analysis of only RCTs, the results showed for gastrointestinal bleeding (RR, 1.31 [0.95, 1.79], P=0.1), for major bleeding (RR, 0.98 [0.76, 1.25], P< 0.00001), and all-cause mortality (RR, 0.89 [0.83, 0.96], P=0.001).
Discussion: Our findings indicate that DOACs are a safer and more effective option than warfarin for reducing the risk of major bleeding and all-cause mortality in older adult patients with AF. They do not impact the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding. This meta-analysis demonstrates the efficacy of DOACs, which is encouraging. More RCTs are needed for better interpretation.
Disclosures:
Hamza Naeem, MD1, Umar Abdul Rehman Khalid, MD1, Ahmad Zain, MD2, Mohammad Maheer Mubashir, 1, Abdul Mueed Bangash, MBBS3, Usama Qamar, MD1, Masood Azhar, MD1, Rida Ayesha Rafique, MD1, Ijlal Akbar Ali, MD4, Muhammad Umair, MD1, Muhammad Shehryar, MD1, Muhammad Bilal Shahid, MBBS1, Usama Ali, MD1, Muhammad Abdullah Javed, MD1. P2446 - Evaluating Gastrointestinal Bleeding Risks: A Meta-Analysis Comparing Direct Oral Anticoagulants and Warfarin in Older Adult Patients With Atrial Fibrillation, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1King Edward Medical University, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 2UChealth Parkview Medical Center, Pueblo, CO; 3Khyber Teaching Hospital, Peshawar, North-West Frontier, Pakistan; 4University of Oklahoma College of Medicine, Oklahoma City, OK
Introduction: The recently published randomized trial Frail-AF raised ambiguity regarding the safety of using direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) over warfarin in older adult patients (≥65) with atrial fibrillation (AF). This meta-analysis aims to evaluate gastrointestinal bleeding, major bleeding, or all-cause mortality in these patients.
Methods: We searched Google Scholar, Scopus, Embase, and Pubmed from inception to June 2024 for relevant publications reporting gastrointestinal bleeding, major bleeding (any bleeding in a critical area or organ), or all-cause mortality. Only studies presenting the clinical outcomes data on older adult patients (≥65) with AF, with patients on either DOACs (Epixaban, Rivaroxaban, or Dabigatran), or warfarin, double-arm studies (randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and retrospective Studies), and those with outcomes given in the form of number-of-events were included. Studies without data on AF, with patient age less than 65 years, or single-arm studies (no comparison group) were excluded. Revman 5.4 was used to analyze the data.
Results: We included 14 studies with a total of 589,262 patients. The pooled risk ratios (RR) with 95% confidence interval for gastrointestinal bleeding was 0.90 [0.67, 1.22], (P = 0.50), for major bleeding, it was 0.75 [0.64, 0.89], (P = 0.0008), for all-cause mortality = 0.68 [0.56, 0.83], (P = 0.0002). DOACs did not significantly reduce the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding compared to warfarin. DOACs demonstrated a statistically significant reduction in major bleeding and all-cause mortality compared to the use of warfarin. In the subgroup sensitivity analysis of only RCTs, the results showed for gastrointestinal bleeding (RR, 1.31 [0.95, 1.79], P=0.1), for major bleeding (RR, 0.98 [0.76, 1.25], P< 0.00001), and all-cause mortality (RR, 0.89 [0.83, 0.96], P=0.001).
Discussion: Our findings indicate that DOACs are a safer and more effective option than warfarin for reducing the risk of major bleeding and all-cause mortality in older adult patients with AF. They do not impact the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding. This meta-analysis demonstrates the efficacy of DOACs, which is encouraging. More RCTs are needed for better interpretation.

Figure: Figure 1: Comparison of Direct Oral Anticoagulants Vs Warfarin for a. Gastrointestinal Bleeding b. Major Bleeding c. All Cause mortality
Disclosures:
Hamza Naeem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Umar Abdul Rehman Khalid indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmad Zain indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammad Maheer Mubashir indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdul Mueed Bangash indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Usama Qamar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Masood Azhar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rida Ayesha Rafique indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ijlal Akbar Ali indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Umair indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Shehryar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Bilal Shahid indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Usama Ali indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Abdullah Javed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hamza Naeem, MD1, Umar Abdul Rehman Khalid, MD1, Ahmad Zain, MD2, Mohammad Maheer Mubashir, 1, Abdul Mueed Bangash, MBBS3, Usama Qamar, MD1, Masood Azhar, MD1, Rida Ayesha Rafique, MD1, Ijlal Akbar Ali, MD4, Muhammad Umair, MD1, Muhammad Shehryar, MD1, Muhammad Bilal Shahid, MBBS1, Usama Ali, MD1, Muhammad Abdullah Javed, MD1. P2446 - Evaluating Gastrointestinal Bleeding Risks: A Meta-Analysis Comparing Direct Oral Anticoagulants and Warfarin in Older Adult Patients With Atrial Fibrillation, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
