Monday Poster Session
Category: Esophagus
P2302 - Successful Medical Management Strategy for Injection Site Intolerance in Dupilumab Therapy
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E

Has Audio

Deva Christine T. Tojong, MD
Medical College of Georgia at Augusta University
Augusta, GA
Presenting Author(s)
Deva Christine T. Tojong, MD1, Gomathy A. Nageswaran, MBBS2, Ronan Calibuso, MD3, Kenneth Vega, MD, FACG1, John Erikson Yap, MD, MBA, FACG4
1Medical College of Georgia at Augusta University, Augusta, GA; 2University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock, AR; 3Jersey City, NJ; 4Metrodora Institute, West Valley City, UT
Introduction: Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE), recognized as a discrete clinical disease in the mid-1990s, has been increasingly identified as a major cause of esophageal disease. Dupilumab, an FDA-approved monoclonal antibody targeting IL-4 and IL-13 receptors, is used to treat EoE. However, its injectable form may cause injection site reactions (ISRs). We report successful management of ISR intolerance in a patient receiving Dupilumab, detailing interventions to mitigate ISR symptoms.
Case Description/Methods: A 32-year-old woman with confirmed EoE following an esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) due to dysphagia was referred for management. On examination, she presented with stable vital signs and unremarkable physical examination. Despite previous treatment attempts with pantoprazole and oral glucocorticoid therapy, symptoms persisted, with repeat EGD revealing persistent esophageal eosinophilia ( >15/hpf). She was prescribed Dupilumab 300mg/2mL injections. However, she encountered significant injection site pain, initially with the pre-filled syringe and later with the pre-filled pen, despite multiple measures to alleviate discomfort. These measures included removing the medication from refrigeration 45 minutes before injection, rotating injection sites, and applying an ice pack 15 minutes before injection, all of which failed to mitigate the pain and injection site redness. Notably, she did not experience any respiratory distress or signs of anaphylaxis. In an attempt to improve medication tolerance, a topical cream containing lidocaine-prilocaine was applied to the injection site 15 minutes before administration. With this intervention, successful medication was achieved with repeat EGD following revealing EoE resolution.
Discussion: Despite advancements in EoE management with FDA-approved medications, challenges arise in patients intolerant to these treatments. Despite proven efficacy, ensuring administration of these medications remains crucial. As healthcare providers, our role extends beyond merely prescribing medications; we are entrusted with facilitating patient adherence to therapy and addressing barriers to treatment intolerance. Adopting a comprehensive approach is imperative, involving measures in technical administration techniques and the careful application of pharmacologic interventions to alleviate intolerable reactions in patients without limiting medication efficacy. Doing so in this case achieved successful resolution of EoE.
Disclosures:
Deva Christine T. Tojong, MD1, Gomathy A. Nageswaran, MBBS2, Ronan Calibuso, MD3, Kenneth Vega, MD, FACG1, John Erikson Yap, MD, MBA, FACG4. P2302 - Successful Medical Management Strategy for Injection Site Intolerance in Dupilumab Therapy, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Medical College of Georgia at Augusta University, Augusta, GA; 2University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock, AR; 3Jersey City, NJ; 4Metrodora Institute, West Valley City, UT
Introduction: Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE), recognized as a discrete clinical disease in the mid-1990s, has been increasingly identified as a major cause of esophageal disease. Dupilumab, an FDA-approved monoclonal antibody targeting IL-4 and IL-13 receptors, is used to treat EoE. However, its injectable form may cause injection site reactions (ISRs). We report successful management of ISR intolerance in a patient receiving Dupilumab, detailing interventions to mitigate ISR symptoms.
Case Description/Methods: A 32-year-old woman with confirmed EoE following an esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) due to dysphagia was referred for management. On examination, she presented with stable vital signs and unremarkable physical examination. Despite previous treatment attempts with pantoprazole and oral glucocorticoid therapy, symptoms persisted, with repeat EGD revealing persistent esophageal eosinophilia ( >15/hpf). She was prescribed Dupilumab 300mg/2mL injections. However, she encountered significant injection site pain, initially with the pre-filled syringe and later with the pre-filled pen, despite multiple measures to alleviate discomfort. These measures included removing the medication from refrigeration 45 minutes before injection, rotating injection sites, and applying an ice pack 15 minutes before injection, all of which failed to mitigate the pain and injection site redness. Notably, she did not experience any respiratory distress or signs of anaphylaxis. In an attempt to improve medication tolerance, a topical cream containing lidocaine-prilocaine was applied to the injection site 15 minutes before administration. With this intervention, successful medication was achieved with repeat EGD following revealing EoE resolution.
Discussion: Despite advancements in EoE management with FDA-approved medications, challenges arise in patients intolerant to these treatments. Despite proven efficacy, ensuring administration of these medications remains crucial. As healthcare providers, our role extends beyond merely prescribing medications; we are entrusted with facilitating patient adherence to therapy and addressing barriers to treatment intolerance. Adopting a comprehensive approach is imperative, involving measures in technical administration techniques and the careful application of pharmacologic interventions to alleviate intolerable reactions in patients without limiting medication efficacy. Doing so in this case achieved successful resolution of EoE.

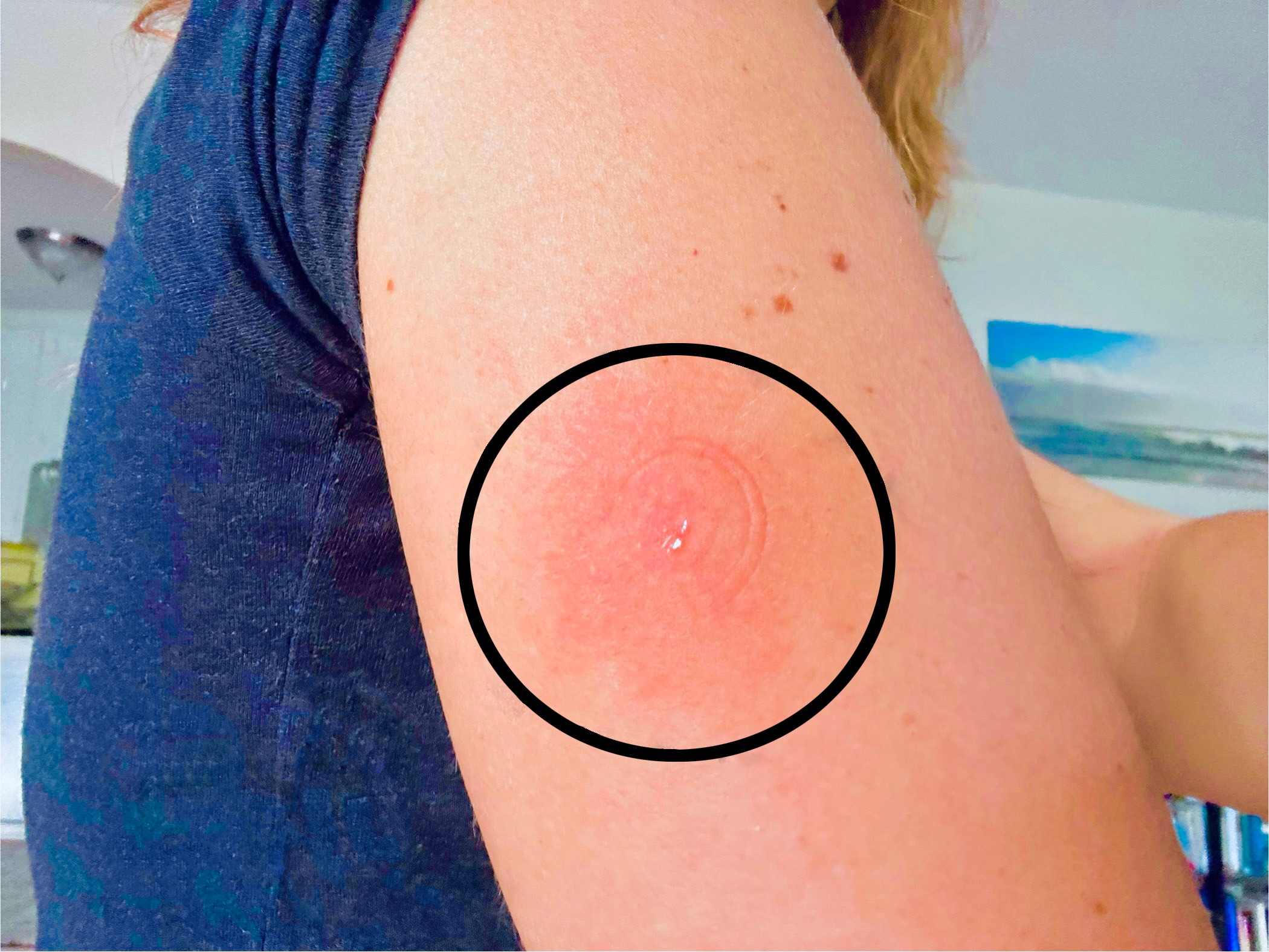
Figure: Presence of a tender, circumscribed, erythematous injection site reaction over patient's right upper arm after utilizing the pre-filled pen of the Dupilumab 300mg/2ml medication despite multiple alleviating measures.
Disclosures:
Deva Christine Tojong indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Gomathy Nageswaran indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ronan Calibuso indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kenneth Vega indicated no relevant financial relationships.
John Erikson Yap indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Deva Christine T. Tojong, MD1, Gomathy A. Nageswaran, MBBS2, Ronan Calibuso, MD3, Kenneth Vega, MD, FACG1, John Erikson Yap, MD, MBA, FACG4. P2302 - Successful Medical Management Strategy for Injection Site Intolerance in Dupilumab Therapy, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
