Sunday Poster Session
Category: Obesity
P1447 - Assessing PPI Administration Strategies to Minimize Marginal Ulceration Complications Following Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass
Sunday, October 27, 2024
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Michael Cymbal, DO
Cleveland Clinic Foundation
Cleveland, OH
Presenting Author(s)
Michael Cymbal, DO1, Anusha Agarwal, MD1, Varun Aitharaju, MD1, Heesoo Yoo, MD1, Alvin Kwon, MD1, Alison Zhao, BA2, Kristelle Imperio-Lagabon, MD1, Stephen Firkins, MD3, Roma Patel, MD4, Bailey Flora, RD1, C Roberto Simon-Linares, MD3
1Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Cleveland, OH; 2Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine, Cleveland, OH; 3Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH; 4Digestive Disease and Surgery Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH
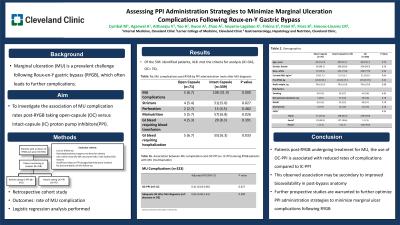
Introduction: Marginal ulceration (MU) is one of the most prevalent complications following Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB). MU can precipitate a cascade of complications, culminating in hospitalizations, procedures, and substantial healthcare costs. Our study aimed to evaluate the association of MU complication rates in post-RYGB taking open-capsule (OC) versus intact-capsule (IC) PPI.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective analysis on adult patients with a history of RYGB following in our Bariatric clinic with evidence of MU on esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) between 1/2013-4/2022. Patients were stratified into two groups, OC-PPI and IC-PPI. PPI details (type, dose, formulation) pre/post-MU. Exclusion criteria included gastric bypass for non-obesity, inadequate PPI data or ulceration details, loss to follow-up, or lack of MU surveillance. The primary outcome was the rate of MU complications, including stricture, perforation, malnutrition, and GI bleeding requiring blood transfusion or hospitalization, between the two groups, which was further analyzed by logistical regression.
Results: Among 594 identified patients, 418 met the criteria for analysis (IC=342, OC=76). Baseline characteristics such as age, race, smoking status, and alcohol use did not significantly differ between groups, except current body mass index (BMI). Complications occurred in 5 patients treated with OC-PPI (7.0%) compared to 108 treated with IC-PPI (31.9%), with (p=0.000). For certain patients, multiple simultaneous complications account for the discrepancy between the case numbers and the total number of patients, as illustrated in Table 1a. Subcategories of complications that demonstrated a significant difference included stricture (p=0.027), malnutrition (p=0.026), and GI bleeding requiring hospitalization (p=0.033). Daily PPI doses were converted to Omeprazole Equivalence (OE) to standardize different PPI agents. The odds ratio (OR) was then calculated, adjusting for the adequacy of OE potency. This showed a decreased association between composite MU complications in the OC-PPI group to IC-PPI by 59% (adjusted OR, 0.41: 95% CI 0.18-0.90, p=0.027).
Discussion: Our findings suggest that in patients post-RYGB undergoing treatment for MU, the use of OC-PPI is associated with significantly reduced rates of complications compared to IC-PPI. This observed association may be secondary to improved bioavailability in the post-bypass anatomy and warrants further investigation.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Michael Cymbal, DO1, Anusha Agarwal, MD1, Varun Aitharaju, MD1, Heesoo Yoo, MD1, Alvin Kwon, MD1, Alison Zhao, BA2, Kristelle Imperio-Lagabon, MD1, Stephen Firkins, MD3, Roma Patel, MD4, Bailey Flora, RD1, C Roberto Simon-Linares, MD3. P1447 - Assessing PPI Administration Strategies to Minimize Marginal Ulceration Complications Following Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Cleveland, OH; 2Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine, Cleveland, OH; 3Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH; 4Digestive Disease and Surgery Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH
Introduction: Marginal ulceration (MU) is one of the most prevalent complications following Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB). MU can precipitate a cascade of complications, culminating in hospitalizations, procedures, and substantial healthcare costs. Our study aimed to evaluate the association of MU complication rates in post-RYGB taking open-capsule (OC) versus intact-capsule (IC) PPI.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective analysis on adult patients with a history of RYGB following in our Bariatric clinic with evidence of MU on esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) between 1/2013-4/2022. Patients were stratified into two groups, OC-PPI and IC-PPI. PPI details (type, dose, formulation) pre/post-MU. Exclusion criteria included gastric bypass for non-obesity, inadequate PPI data or ulceration details, loss to follow-up, or lack of MU surveillance. The primary outcome was the rate of MU complications, including stricture, perforation, malnutrition, and GI bleeding requiring blood transfusion or hospitalization, between the two groups, which was further analyzed by logistical regression.
Results: Among 594 identified patients, 418 met the criteria for analysis (IC=342, OC=76). Baseline characteristics such as age, race, smoking status, and alcohol use did not significantly differ between groups, except current body mass index (BMI). Complications occurred in 5 patients treated with OC-PPI (7.0%) compared to 108 treated with IC-PPI (31.9%), with (p=0.000). For certain patients, multiple simultaneous complications account for the discrepancy between the case numbers and the total number of patients, as illustrated in Table 1a. Subcategories of complications that demonstrated a significant difference included stricture (p=0.027), malnutrition (p=0.026), and GI bleeding requiring hospitalization (p=0.033). Daily PPI doses were converted to Omeprazole Equivalence (OE) to standardize different PPI agents. The odds ratio (OR) was then calculated, adjusting for the adequacy of OE potency. This showed a decreased association between composite MU complications in the OC-PPI group to IC-PPI by 59% (adjusted OR, 0.41: 95% CI 0.18-0.90, p=0.027).
Discussion: Our findings suggest that in patients post-RYGB undergoing treatment for MU, the use of OC-PPI is associated with significantly reduced rates of complications compared to IC-PPI. This observed association may be secondary to improved bioavailability in the post-bypass anatomy and warrants further investigation.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Michael Cymbal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anusha Agarwal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Varun Aitharaju indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Heesoo Yoo indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Alvin Kwon indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Alison Zhao indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kristelle Imperio-Lagabon indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Stephen Firkins indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Roma Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bailey Flora indicated no relevant financial relationships.
C Roberto Simon-Linares indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Michael Cymbal, DO1, Anusha Agarwal, MD1, Varun Aitharaju, MD1, Heesoo Yoo, MD1, Alvin Kwon, MD1, Alison Zhao, BA2, Kristelle Imperio-Lagabon, MD1, Stephen Firkins, MD3, Roma Patel, MD4, Bailey Flora, RD1, C Roberto Simon-Linares, MD3. P1447 - Assessing PPI Administration Strategies to Minimize Marginal Ulceration Complications Following Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
