Sunday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P1277 - Liver Transplantation After Successful Downstaging of Multifocal Hepatocellular Carcinoma With Marked AFP Elevation Using Interventional Immuno-oncology
Sunday, October 27, 2024
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio
- SK
Shiva Kumar, MD, MHA
Cleveland Clinic
Abu Dhabi, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates
Presenting Author(s)
Award: ACG Case Reports Journal Award
Award: Presidential Poster Award
Shiva Kumar, MD, MHA
Cleveland Clinic, Abu Dhabi, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates
Introduction: A significant proportion of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) exceed Milan criteria for liver transplant (LT). Serum biomarker alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) is a well-known prognostic marker for HCC and patients with baseline AFP levels exceeding 1000 ng/mL are precluded from LT without successful downstaging. Immunotherapy has emerged as the first line option for those with advanced HCC, but it’s efficacy and safety in patients awaiting LT remains unclear. Combination of loco-regional therapy (LRT) and immunotherapy (recently termed interventional immuno-oncology) has shown promise in downstaging patients with HCC exceeding Milan criteria. We present a case of multifocal HCC with marked AFP elevation successfully downstaged to LT using interventional immuno-oncology.
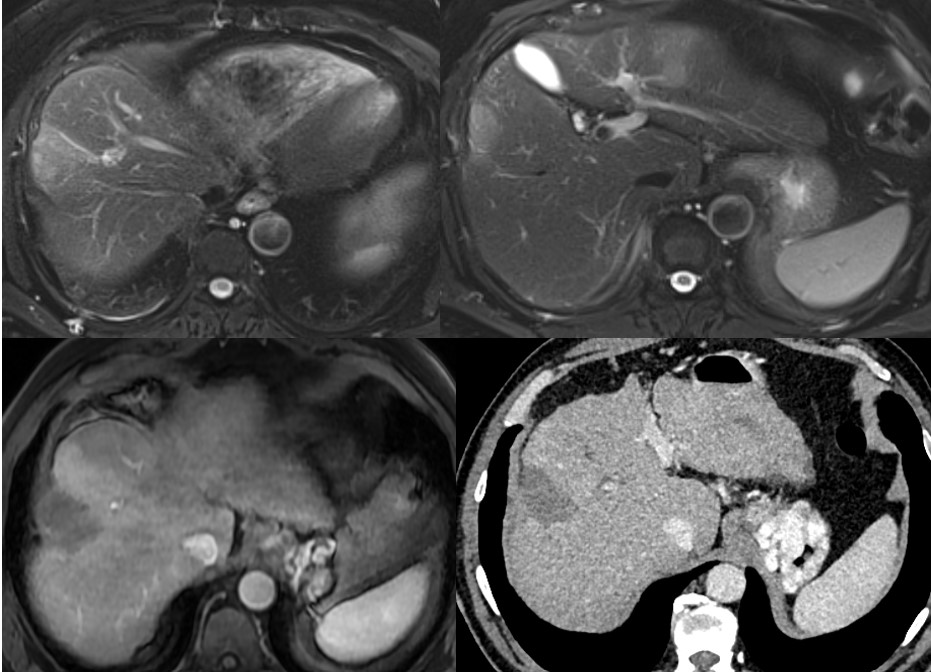
Case Description/Methods: A 67 year old male with history of cirrhosis secondary to HCV was noted to have multiple liver lesions on ultrasonography. MRI revealed lesions with imaging features of HCC (LI-RADS 5) in segments VIII (4.7 cm) and II (1.7 cm) with multiple smaller nodules with indeterminate imaging characteristics (figure – upper panel). AFP was markedly elevated at 2426 ng/mL. He subsequently underwent sequential right and left lobe Yttrium-90 trans-arterial radioembolization, with concomitant initiation of immunotherapy using Atezolizimab and Bevacizumab. Follow up MRI and CT 4 months later showed significant interval improvement and necrosis without arterial enhancement (figure – lower panel). AFP declined dramatically, normalized at 5 ng/mL and remained persistently within normal limits. Patient was listed for and subsequently underwent deceased donor LT, 2 months after last dose of immunotherapy. Explant revealed near complete necrosis of all lesions with just 2 diminutive foci of viable tumor 0.3 and 0.2 cm in segments V and VIII. He remains recurrence free 6 months post-LT (with normal AFP) and without any episodes of rejection.
Discussion: Synergistic effect of combined LRT and immunotherapy-based approaches may be due to increase in tumor immunogenicity by LRT, thereby enhancing the effect of immunotherapy. Given risk of rejection, optimal interval between immunotherapy and LT remains unclear. Further study is needed to explore its safety and clarify long-term oncologic outcomes in a pre-LT setting and identify biomarkers to define immunotherapeutic response. Interventional immuno-oncology holds great potential as a therapeutic option for downstaging patients with HCC that exceed criteria for transplant.
Disclosures:
Shiva Kumar, MD, MHA. P1277 - Liver Transplantation After Successful Downstaging of Multifocal Hepatocellular Carcinoma With Marked AFP Elevation Using Interventional Immuno-oncology, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
Award: Presidential Poster Award
Shiva Kumar, MD, MHA
Cleveland Clinic, Abu Dhabi, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates
Introduction: A significant proportion of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) exceed Milan criteria for liver transplant (LT). Serum biomarker alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) is a well-known prognostic marker for HCC and patients with baseline AFP levels exceeding 1000 ng/mL are precluded from LT without successful downstaging. Immunotherapy has emerged as the first line option for those with advanced HCC, but it’s efficacy and safety in patients awaiting LT remains unclear. Combination of loco-regional therapy (LRT) and immunotherapy (recently termed interventional immuno-oncology) has shown promise in downstaging patients with HCC exceeding Milan criteria. We present a case of multifocal HCC with marked AFP elevation successfully downstaged to LT using interventional immuno-oncology.
Case Description/Methods: A 67 year old male with history of cirrhosis secondary to HCV was noted to have multiple liver lesions on ultrasonography. MRI revealed lesions with imaging features of HCC (LI-RADS 5) in segments VIII (4.7 cm) and II (1.7 cm) with multiple smaller nodules with indeterminate imaging characteristics (figure – upper panel). AFP was markedly elevated at 2426 ng/mL. He subsequently underwent sequential right and left lobe Yttrium-90 trans-arterial radioembolization, with concomitant initiation of immunotherapy using Atezolizimab and Bevacizumab. Follow up MRI and CT 4 months later showed significant interval improvement and necrosis without arterial enhancement (figure – lower panel). AFP declined dramatically, normalized at 5 ng/mL and remained persistently within normal limits. Patient was listed for and subsequently underwent deceased donor LT, 2 months after last dose of immunotherapy. Explant revealed near complete necrosis of all lesions with just 2 diminutive foci of viable tumor 0.3 and 0.2 cm in segments V and VIII. He remains recurrence free 6 months post-LT (with normal AFP) and without any episodes of rejection.
Discussion: Synergistic effect of combined LRT and immunotherapy-based approaches may be due to increase in tumor immunogenicity by LRT, thereby enhancing the effect of immunotherapy. Given risk of rejection, optimal interval between immunotherapy and LT remains unclear. Further study is needed to explore its safety and clarify long-term oncologic outcomes in a pre-LT setting and identify biomarkers to define immunotherapeutic response. Interventional immuno-oncology holds great potential as a therapeutic option for downstaging patients with HCC that exceed criteria for transplant.

Figure: Liver protocol MRI prior to radioembolization and immunotherapy demonstrating multifocal HCC (upper panel) and post-treatment MRI and CT showing no residual disease (lower panel).
Disclosures:
Shiva Kumar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shiva Kumar, MD, MHA. P1277 - Liver Transplantation After Successful Downstaging of Multifocal Hepatocellular Carcinoma With Marked AFP Elevation Using Interventional Immuno-oncology, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.

