Sunday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P1289 - A Case of Primary Hepatic Sarcoidosis
Sunday, October 27, 2024
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Hiba Hameed Chagla, MD
Penn Medicine
Philadelphia, PA
Presenting Author(s)
Hiba Hameed Chagla, MD1, Anila Vasireddy, MD2, Veena Madhu, MD1, Michael Demarco, DO1, Ali Ismail, MD1
1Penn Medicine, Philadelphia, PA; 2University of Pennsylvania Health System, Philadelphia, PA
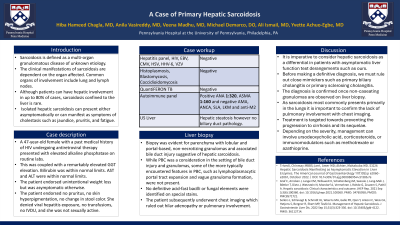
Introduction: Sarcoidosis is defined as a multi-organ granulomatous disease of unknown etiology. The clinical manifestations of sarcoidosis are dependent on the organ affected. Common organs of involvement include lung and lymph nodes. Although patients can have hepatic involvement in up to 80% of cases, sarcoidosis confined to the liver is rare. Isolated hepatic sarcoidosis can present either asymptomatically or can manifest as symptoms of cholestasis such as jaundice, pruritis, and fatigue.
Case Description/Methods: A 47-year-old female with past medical history of HIV undergoing antiretroviral therapy presented with elevated alkaline phosphatase on routine labs. This was coupled with a remarkably elevated GGT elevation. Bilirubin was within normal limits. AST and ALT were within normal limits. The patient endorsed unintentional weight loss but was asymptomatic otherwise. No pruritus, no skin hyperpigmentation, no change in stool color. The patient denied viral hepatitis exposure, no transfusions, no IVDU, and she was not sexually active. She underwent a full workup. Viral and fungal infection screen was negative. Autoimmune workup with positive ANA and ASMA and negative AMA. US showed hepatic steatosis however no biliary duct pathology. Given unremarkable workup patient underwent liver biopsy which was evident for non-caseating epithelioid granulomas suggestive of hepatic sarcoidosis. She then underwent chest imaging which ruled out hilar adenopathy or pulmonary involvement.
Discussion: It is imperative to consider hepatic sarcoidosis as a differential in patients with asymptomatic liver function test derangements such as ours. Prior to making a definitive diagnosis we must rule out close mimickers such as primary biliary cholangitis or primary sclerosing cholangitis. The diagnosis is confirmed once non-caseating granulomas are observed on liver biopsy. As sarcoidosis most commonly presents primarily in the lungs it is important to confirm lack of pulmonary involvement with chest imaging. Treatment is targeted towards preventing progression to cirrhosis and its sequelae. Depending on the severity, management can involve urso-deoxycholic acid, corticosteroids, or immunomodulators such as methotrexate or azathioprine.
Disclosures:
Hiba Hameed Chagla, MD1, Anila Vasireddy, MD2, Veena Madhu, MD1, Michael Demarco, DO1, Ali Ismail, MD1. P1289 - A Case of Primary Hepatic Sarcoidosis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Penn Medicine, Philadelphia, PA; 2University of Pennsylvania Health System, Philadelphia, PA
Introduction: Sarcoidosis is defined as a multi-organ granulomatous disease of unknown etiology. The clinical manifestations of sarcoidosis are dependent on the organ affected. Common organs of involvement include lung and lymph nodes. Although patients can have hepatic involvement in up to 80% of cases, sarcoidosis confined to the liver is rare. Isolated hepatic sarcoidosis can present either asymptomatically or can manifest as symptoms of cholestasis such as jaundice, pruritis, and fatigue.
Case Description/Methods: A 47-year-old female with past medical history of HIV undergoing antiretroviral therapy presented with elevated alkaline phosphatase on routine labs. This was coupled with a remarkably elevated GGT elevation. Bilirubin was within normal limits. AST and ALT were within normal limits. The patient endorsed unintentional weight loss but was asymptomatic otherwise. No pruritus, no skin hyperpigmentation, no change in stool color. The patient denied viral hepatitis exposure, no transfusions, no IVDU, and she was not sexually active. She underwent a full workup. Viral and fungal infection screen was negative. Autoimmune workup with positive ANA and ASMA and negative AMA. US showed hepatic steatosis however no biliary duct pathology. Given unremarkable workup patient underwent liver biopsy which was evident for non-caseating epithelioid granulomas suggestive of hepatic sarcoidosis. She then underwent chest imaging which ruled out hilar adenopathy or pulmonary involvement.
Discussion: It is imperative to consider hepatic sarcoidosis as a differential in patients with asymptomatic liver function test derangements such as ours. Prior to making a definitive diagnosis we must rule out close mimickers such as primary biliary cholangitis or primary sclerosing cholangitis. The diagnosis is confirmed once non-caseating granulomas are observed on liver biopsy. As sarcoidosis most commonly presents primarily in the lungs it is important to confirm lack of pulmonary involvement with chest imaging. Treatment is targeted towards preventing progression to cirrhosis and its sequelae. Depending on the severity, management can involve urso-deoxycholic acid, corticosteroids, or immunomodulators such as methotrexate or azathioprine.
Disclosures:
Hiba Hameed Chagla indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anila Vasireddy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Veena Madhu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Michael Demarco indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ali Ismail indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hiba Hameed Chagla, MD1, Anila Vasireddy, MD2, Veena Madhu, MD1, Michael Demarco, DO1, Ali Ismail, MD1. P1289 - A Case of Primary Hepatic Sarcoidosis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.

