Sunday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P0829 - Efficacy and Safety Profile of Small Molecules for Induction and Maintenance of Remission in Ulcerative Colitis: A Systematic Review of Randomised Control Trials
Sunday, October 27, 2024
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E

Has Audio
- MF
Mahek Fatima, MBBS
Osmania General Hospital and Medical College
Hyderabad, Telangana, India
Presenting Author(s)
Mahek Fatima, MBBS1, Archana Priyadarsini, MBBS2, Ashwith Reddy Gaddam, MD3, Sreeja Cherukuru, MBBS4, Sree Maneesha Sunkara, MBBS, MPH.5, Binay K. Panjiyar, MBBS6
1Osmania General Hospital and Medical College, Hyderabad, Telangana, India; 2Dr Somervell Memorial CSI Medical College, Missouri City, TX; 3University of Kansas Medical Center, Kamareddy, Telangana, India; 4Sri Venkateswara Medical College, Tirupati, Andhra Pradesh, India; 5Malla Reddy Institute of Medical Sciences, Ashland, MA; 6Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA
Introduction: Ulcerative colitis(UC) is a chronic disease, which can significantly impair health-related quality of life(HRQoL). With its natural remitting and relapsing course, the treatment is often challenging. Small molecules have emerged as a new potential treatment for the induction and maintenance of remission in moderate to severe ulcerative colitis. In this study, we aim to review the clinical trials of small molecules to determine the effectiveness and safety concerns of these agents in the management of ulcerative colitis.
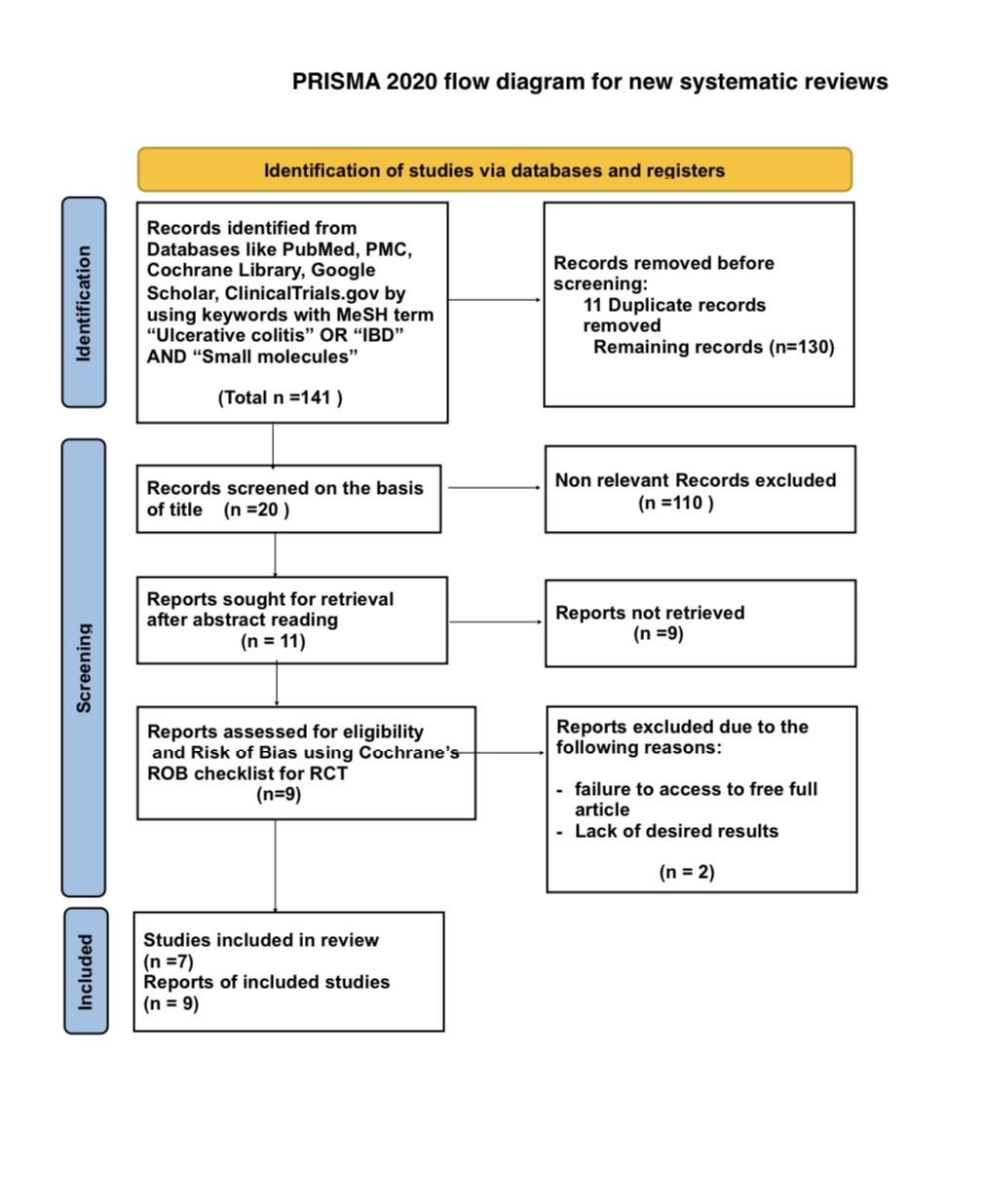
Methods: The electronic databases PubMed including PubMed, PMC, Google Scholar, Cochrane Library, and clinicaltrials.gov were queried from June 2014 until June 2024 using a comprehensive search strategy. Only studies that were randomized, conducted on adult subjects with UC and published as full manuscripts were included. Risk of Bias(ROB) of the included RCTs was assessed using Cochrane’s ROB checklist.
Results: Among 6845 pooled patients from 9 RCTs, small molecules (including tofacitinib, ritlecitinib,brepocitinib,upadacitinib,filgotinib,etrasimod) were superior to placebo in the management of UC for induction as well as maintenance of remission. These agents are effective resulting in early clinical remission, as determined by the assessment of total Mayo score and endoscopic normalization and they also help achieve corticosteroid-free remission. Further assessment showed significantly improved HRQoL and IBDQ (Inflammatory Bowel Disease Questionnaire) outcomes. Infections and infestations, mild anaemia, headaches, and herpes zoster infection were the frequently reported adverse effects. Elevated creatinine kinase levels with tofacitinib and sinus bradycardia with etrasimod were the noteworthy AEs.
Discussion: Small molecules appear promising for the induction and maintenance of clinical remission in UC. They significantly improve the HRQoL index and reduce corticosteroid dependence. Tofacitinib has been thoroughly studied and established as an effective agent with minimal safety concerns; however, for the other newer agents, rigorous studies and trials are warranted.
Disclosures:
Mahek Fatima, MBBS1, Archana Priyadarsini, MBBS2, Ashwith Reddy Gaddam, MD3, Sreeja Cherukuru, MBBS4, Sree Maneesha Sunkara, MBBS, MPH.5, Binay K. Panjiyar, MBBS6. P0829 - Efficacy and Safety Profile of Small Molecules for Induction and Maintenance of Remission in Ulcerative Colitis: A Systematic Review of Randomised Control Trials, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Osmania General Hospital and Medical College, Hyderabad, Telangana, India; 2Dr Somervell Memorial CSI Medical College, Missouri City, TX; 3University of Kansas Medical Center, Kamareddy, Telangana, India; 4Sri Venkateswara Medical College, Tirupati, Andhra Pradesh, India; 5Malla Reddy Institute of Medical Sciences, Ashland, MA; 6Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA
Introduction: Ulcerative colitis(UC) is a chronic disease, which can significantly impair health-related quality of life(HRQoL). With its natural remitting and relapsing course, the treatment is often challenging. Small molecules have emerged as a new potential treatment for the induction and maintenance of remission in moderate to severe ulcerative colitis. In this study, we aim to review the clinical trials of small molecules to determine the effectiveness and safety concerns of these agents in the management of ulcerative colitis.
Methods: The electronic databases PubMed including PubMed, PMC, Google Scholar, Cochrane Library, and clinicaltrials.gov were queried from June 2014 until June 2024 using a comprehensive search strategy. Only studies that were randomized, conducted on adult subjects with UC and published as full manuscripts were included. Risk of Bias(ROB) of the included RCTs was assessed using Cochrane’s ROB checklist.
Results: Among 6845 pooled patients from 9 RCTs, small molecules (including tofacitinib, ritlecitinib,brepocitinib,upadacitinib,filgotinib,etrasimod) were superior to placebo in the management of UC for induction as well as maintenance of remission. These agents are effective resulting in early clinical remission, as determined by the assessment of total Mayo score and endoscopic normalization and they also help achieve corticosteroid-free remission. Further assessment showed significantly improved HRQoL and IBDQ (Inflammatory Bowel Disease Questionnaire) outcomes. Infections and infestations, mild anaemia, headaches, and herpes zoster infection were the frequently reported adverse effects. Elevated creatinine kinase levels with tofacitinib and sinus bradycardia with etrasimod were the noteworthy AEs.
Discussion: Small molecules appear promising for the induction and maintenance of clinical remission in UC. They significantly improve the HRQoL index and reduce corticosteroid dependence. Tofacitinib has been thoroughly studied and established as an effective agent with minimal safety concerns; however, for the other newer agents, rigorous studies and trials are warranted.

Figure: PRISMA flow chart
Disclosures:
Mahek Fatima indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Archana Priyadarsini indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ashwith Reddy Gaddam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sreeja Cherukuru indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sree Maneesha Sunkara indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Binay Panjiyar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mahek Fatima, MBBS1, Archana Priyadarsini, MBBS2, Ashwith Reddy Gaddam, MD3, Sreeja Cherukuru, MBBS4, Sree Maneesha Sunkara, MBBS, MPH.5, Binay K. Panjiyar, MBBS6. P0829 - Efficacy and Safety Profile of Small Molecules for Induction and Maintenance of Remission in Ulcerative Colitis: A Systematic Review of Randomised Control Trials, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
