Sunday Poster Session
Category: Esophagus
P0558 - Drinking Piping Hot Tea Increases Risk of Esophageal Cancer
Sunday, October 27, 2024
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio
.jpg)
Taleen Ashikian
University of Montreal
Montreal, QC, Canada
Presenting Author(s)
Taleen Ashikian, 1, Manuel Babaian, MD2
1University of Montreal, Montreal, PQ, Canada; 2Holy Cross Hospital, Parkland, FL
Introduction: Squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus usually has been historically associated with well described risk factors. Here we present a patient who developed malignancy in the absence of most of the known risk factors except for admitted prolonged use of very hot beverages.
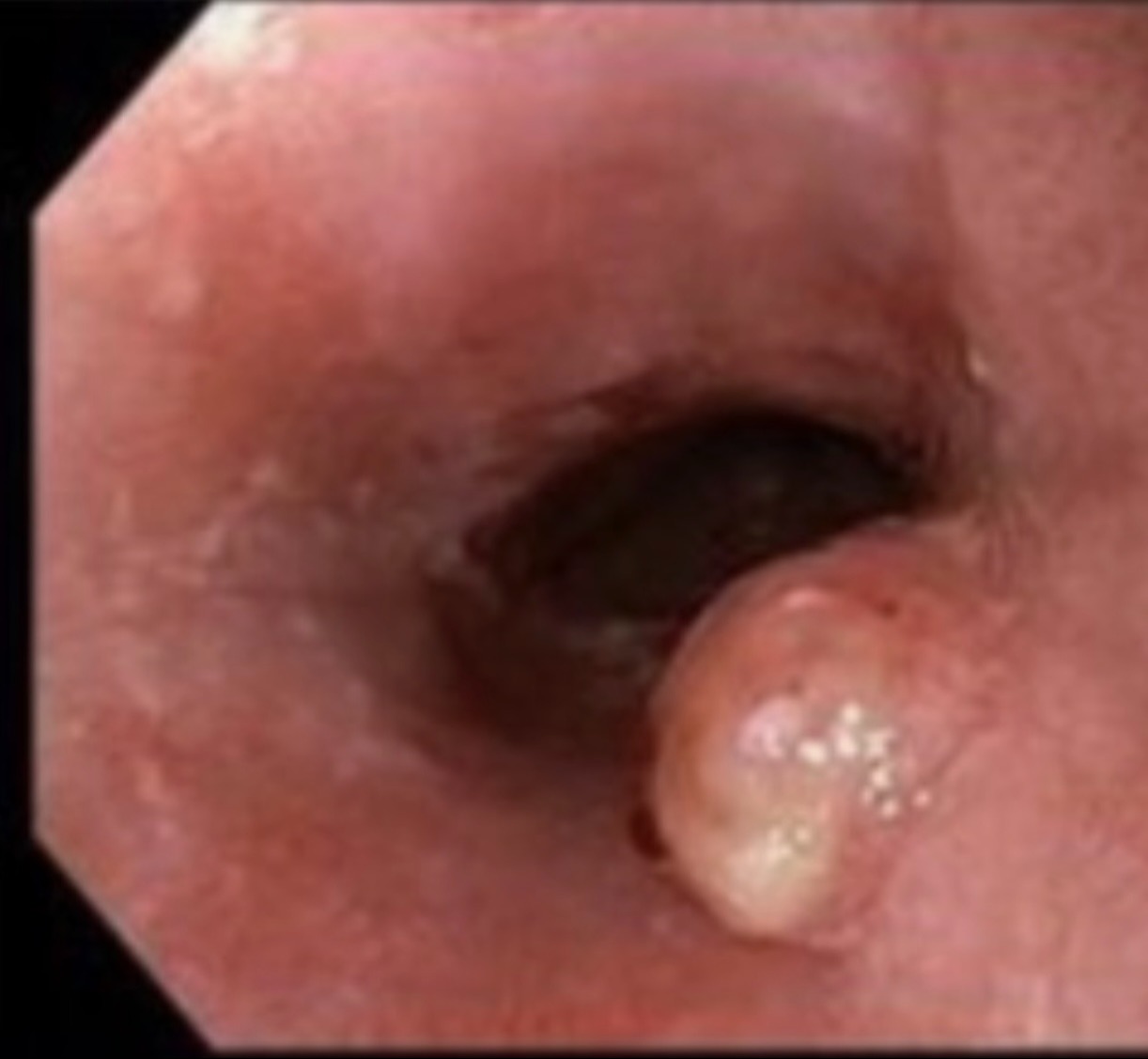
Case Description/Methods: Our patient is a 73 year old woman who previously had no significant existing medical conditions, who complained of slow progressing dysphagia to mostly solid food for a few weeks. The patient then underwent EGD which revealed a 3 cm sub-obstructing lesion in the proximal esophagus (see image attached) and biopsies confirmed moderately differentiated squamous cell carcinoma with local invasion. The patient underwent a combination of chemo and radiation therapy which successfully irradicated the lesion as proven on a subsequent endoscopy.
Discussion: Upon further more detailed questioning, the patient specifically denied any smoking or alcohol use at any point in her life. Being from the region of the Caucasus, the patient did admit to prolonged daily use of very hot tea since her teenage years. Epidemiologic studies have shown an increase in risk of developing esophageal cancer while using hot beverages over prolonged period. In particular, there was a large meta-analysis which reviewed 536 articles in 2009 from the International Journal of Cancer. After inclusion criteria were met, 77 articles were studied. This revealed that high/temperature beverage drinking increases the risk of esophageal cancer. Individuals from certain parts of the world that are known to consume very hot beverages including tea and coffee should be screened for and given recommendations to modify their behavior to reduce the risk of further irritation of the esophagus.
Reference:
F. Islami et al, High-Temperature beverages and Foods and Esophageal Cancer Risk - A Systematic Review, 2009, August 1;125(3): 491-524
Disclosures:
Taleen Ashikian, 1, Manuel Babaian, MD2. P0558 - Drinking Piping Hot Tea Increases Risk of Esophageal Cancer, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of Montreal, Montreal, PQ, Canada; 2Holy Cross Hospital, Parkland, FL
Introduction: Squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus usually has been historically associated with well described risk factors. Here we present a patient who developed malignancy in the absence of most of the known risk factors except for admitted prolonged use of very hot beverages.
Case Description/Methods: Our patient is a 73 year old woman who previously had no significant existing medical conditions, who complained of slow progressing dysphagia to mostly solid food for a few weeks. The patient then underwent EGD which revealed a 3 cm sub-obstructing lesion in the proximal esophagus (see image attached) and biopsies confirmed moderately differentiated squamous cell carcinoma with local invasion. The patient underwent a combination of chemo and radiation therapy which successfully irradicated the lesion as proven on a subsequent endoscopy.
Discussion: Upon further more detailed questioning, the patient specifically denied any smoking or alcohol use at any point in her life. Being from the region of the Caucasus, the patient did admit to prolonged daily use of very hot tea since her teenage years. Epidemiologic studies have shown an increase in risk of developing esophageal cancer while using hot beverages over prolonged period. In particular, there was a large meta-analysis which reviewed 536 articles in 2009 from the International Journal of Cancer. After inclusion criteria were met, 77 articles were studied. This revealed that high/temperature beverage drinking increases the risk of esophageal cancer. Individuals from certain parts of the world that are known to consume very hot beverages including tea and coffee should be screened for and given recommendations to modify their behavior to reduce the risk of further irritation of the esophagus.
Reference:
F. Islami et al, High-Temperature beverages and Foods and Esophageal Cancer Risk - A Systematic Review, 2009, August 1;125(3): 491-524

Figure: Squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus
Disclosures:
Taleen Ashikian indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Manuel Babaian indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Taleen Ashikian, 1, Manuel Babaian, MD2. P0558 - Drinking Piping Hot Tea Increases Risk of Esophageal Cancer, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
