Sunday Poster Session
Category: Endoscopy Video Forum
P0461 - Safety and Efficacy of Lumen Apposing Metal Stents for Management of Late Refractory Gastro-Jejunal Strictures in Patients With Roux-en-Y gastric bypass
Sunday, October 27, 2024
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E

Has Audio

Alejandra Méndez, MD
West Virginia University
Morgantown, WV
Presenting Author(s)
Alejandra Méndez, MD, Rohit Agrawal, MD, Soban Maan, MD, Mouaz Haffar, MD, Ethan M. Cohen, MD, Ayowumi Adekolu, MD, Matthew Krafft, MD, Shyam Thakkar, MD, Shailendra Singh, MD
West Virginia University, Morgantown, WV
Introduction: Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) related late gastro-jejunal (GJ) strictures are often resistant to endoscopic balloon dilations. Lumen-apposing metal stents (LAMSs) have been used to treat benign strictures with favorable results. However, the data remains limited to justify LAMS use for management of post-RYGB late GJ strictures. We aim to evaluate the safety and efficacy of LAMS placement for the management of late GJ strictures that are refractory to balloon dilations in post-RYGB patients.
Case Description/Methods: This was a single center retrospective study that included all post-RYGB patients who underwent LAMS placement for management of late GJ strictures that had previously failed balloon dilations. Primary outcomes were technical and clinical success, and secondary outcomes were LAMS-related adverse events.
Discussion: A total of 28 patients underwent LAMS placement for management of GJ strictures. Median age was 60.5 (IQR: 50.5, 67.0) years and majority were females (27, 96.4%). Median interval between surgery and first diagnosis of GJ stricture was 13 years (IQR: 7,17.5). 20 X 10 mm LAMS was the most used stent (n=24, 85.7%). The median procedure time was 23.5 (IQR: 14.5,32.0) minutes. Technical and short-term clinical success of LAMS placement was 100% (95% CI: 87.9 – 100.0). Long term success was achieved in 19 out of 25 patients (76.0%, 95% CI: 56.6 – 88.5) that had over 3 months follow up after LAMS removal. Stent migration was noted in 2 (7.1%) patients, and 1 (3.6%) patient each experienced pain and minor bleeding without the need for additional interventions. No patient in our cohort required surgical revision of GJ anastomosis.
Placement of LAMS is safe, technically feasible, and associated with a high clinical success rate in patients with late GJ strictures after RYGB who have failed prior balloon dilations. Placement of LAMS can be considered early in patients requiring multiple balloon dilations.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Alejandra Méndez, MD, Rohit Agrawal, MD, Soban Maan, MD, Mouaz Haffar, MD, Ethan M. Cohen, MD, Ayowumi Adekolu, MD, Matthew Krafft, MD, Shyam Thakkar, MD, Shailendra Singh, MD. P0461 - Safety and Efficacy of Lumen Apposing Metal Stents for Management of Late Refractory Gastro-Jejunal Strictures in Patients With Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
West Virginia University, Morgantown, WV
Introduction: Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) related late gastro-jejunal (GJ) strictures are often resistant to endoscopic balloon dilations. Lumen-apposing metal stents (LAMSs) have been used to treat benign strictures with favorable results. However, the data remains limited to justify LAMS use for management of post-RYGB late GJ strictures. We aim to evaluate the safety and efficacy of LAMS placement for the management of late GJ strictures that are refractory to balloon dilations in post-RYGB patients.
Case Description/Methods: This was a single center retrospective study that included all post-RYGB patients who underwent LAMS placement for management of late GJ strictures that had previously failed balloon dilations. Primary outcomes were technical and clinical success, and secondary outcomes were LAMS-related adverse events.
Discussion: A total of 28 patients underwent LAMS placement for management of GJ strictures. Median age was 60.5 (IQR: 50.5, 67.0) years and majority were females (27, 96.4%). Median interval between surgery and first diagnosis of GJ stricture was 13 years (IQR: 7,17.5). 20 X 10 mm LAMS was the most used stent (n=24, 85.7%). The median procedure time was 23.5 (IQR: 14.5,32.0) minutes. Technical and short-term clinical success of LAMS placement was 100% (95% CI: 87.9 – 100.0). Long term success was achieved in 19 out of 25 patients (76.0%, 95% CI: 56.6 – 88.5) that had over 3 months follow up after LAMS removal. Stent migration was noted in 2 (7.1%) patients, and 1 (3.6%) patient each experienced pain and minor bleeding without the need for additional interventions. No patient in our cohort required surgical revision of GJ anastomosis.
Placement of LAMS is safe, technically feasible, and associated with a high clinical success rate in patients with late GJ strictures after RYGB who have failed prior balloon dilations. Placement of LAMS can be considered early in patients requiring multiple balloon dilations.

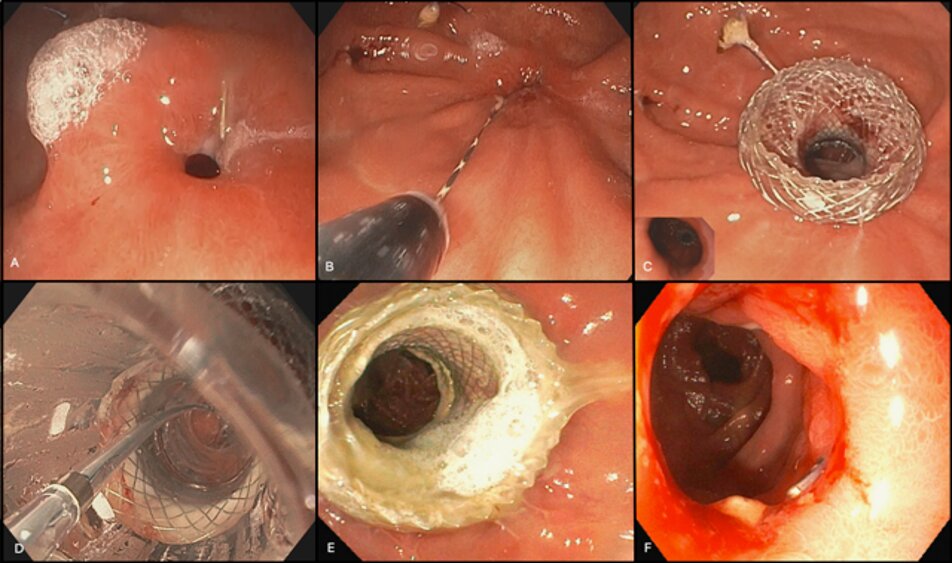
Figure: Figure 1. Placement and removal of LAMS across severe gastrojejunal stricture. A. Severe refractory gastrojejunal stricture. B. Placement of LAMS catheter over guidewire. C. LAMS placement across gastrojejunal stricture. D. Dilation of LAMS. E. LAMS on follow up EGD. F. Patent gastrojejunal stenosis post LAMS removal.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Alejandra Méndez indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rohit Agrawal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Soban Maan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mouaz Haffar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ethan Cohen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ayowumi Adekolu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Matthew Krafft indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shyam Thakkar: Boston Scientific – Consultant. Guide Point – Consultant. Iterative Scopes – Consultant. Medtronic – Consultant. Steris – Consultant.
Shailendra Singh: Apollo Endosurgery – Consultant. Boston Scientific – Consultant. Fujifilm Endoscopy – Consultant.
Alejandra Méndez, MD, Rohit Agrawal, MD, Soban Maan, MD, Mouaz Haffar, MD, Ethan M. Cohen, MD, Ayowumi Adekolu, MD, Matthew Krafft, MD, Shyam Thakkar, MD, Shailendra Singh, MD. P0461 - Safety and Efficacy of Lumen Apposing Metal Stents for Management of Late Refractory Gastro-Jejunal Strictures in Patients With Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.

