Sunday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P0084 - Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma With Unusual Spread to the Pancreas, Biliary System, Ampulla of Vater, and Stomach
Sunday, October 27, 2024
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Ade Waterman, MBChB
MedStar Georgetown University Hospital
Washington, DC
Presenting Author(s)
Ade Waterman, MBChB, Srikar Reddy, MD, Chalhoub Walid, MD
MedStar Georgetown University Hospital, Washington, DC
Introduction: This report details the management of a 74-year-old male with metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) treated initially with nephrectomy and later systemic therapies. The disease exhibited unusual spread to the pancreas, biliary system and stomach.
Case Description/Methods:The patient was diagnosed with a large right kidney mass in October 2012, treated with laparoscopic adrenonephrectomy. Pathology revealed ccRCC with negative margins. Disease progression in May 2015 included metastases to the lungs, mediastinum, and pancreas. Over the years, treatments included multiple systemic therapies with varying success and adverse events.
MedStar Georgetown University Hospital, Washington, DC
Introduction: This report details the management of a 74-year-old male with metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) treated initially with nephrectomy and later systemic therapies. The disease exhibited unusual spread to the pancreas, biliary system and stomach.
Case Description/Methods:
The patient was diagnosed with a large right kidney mass in October 2012, treated with laparoscopic adrenonephrectomy. Pathology revealed ccRCC with negative margins. Disease progression in May 2015 included metastases to the lungs, mediastinum, and pancreas. Over the years, treatments included multiple systemic therapies with varying success and adverse events.
In December 2021, the patient presented with acute cholangitis, prompting endoscopic evaluation. The patient subsequently required seven ERCPs between December 2021 and March 2024 due to recurrent acute cholangitis. Below are highlights of two of these ERCPs:
December 2021
Findings: Significant biliary dilation proximal to distal duct narrowing.
Intervention: Pus and debris extraction; fully covered metal stent placed.
March 2024
Findings: Periampullary abnormal tissue growth, multiple gastric polyps.
Intervention: Stent removal; balloon sweep to remove sludge/debris.
Pathology: Gastric polyp biopsy revealed metastatic ccRCC.
Discussion: GI metastases from RCC are rare, affecting 1.6% of metastatic cases, primarily in the duodenum (50%) and stomach (41.6%). Pancreatic metastases account for 2-5% of pancreatic neoplasms and can appear decades post-diagnosis.
Metastatic disease should be considered in RCC patients presenting with cholangitis. Hepatobiliary involvement in metastatic RCC often requires frequent ERCPs for biliary obstructions. This case involved multiple stent placements to maintain biliary drainage and prevent cholangitis. Surgical intervention is often unfeasible and as such, biliary stenting is crucial for palliation. Fully covered metal stents offering longer patency and fewer changes than plastic stents. Despite this, complications like stent migration and clogging are common.
Patient Update
The patient’s therapy was switched to lenvatinib and noted to have stable biliary disease with functioning stents as demonstrated by stable liver function tests (LFTs) and serial CT scans.
Conclusion
Metastatic RCC with gastrointestinal involvement poses significant management challenges. Regular monitoring and timely interventions are crucial to manage complications and maintain patient quality of life.
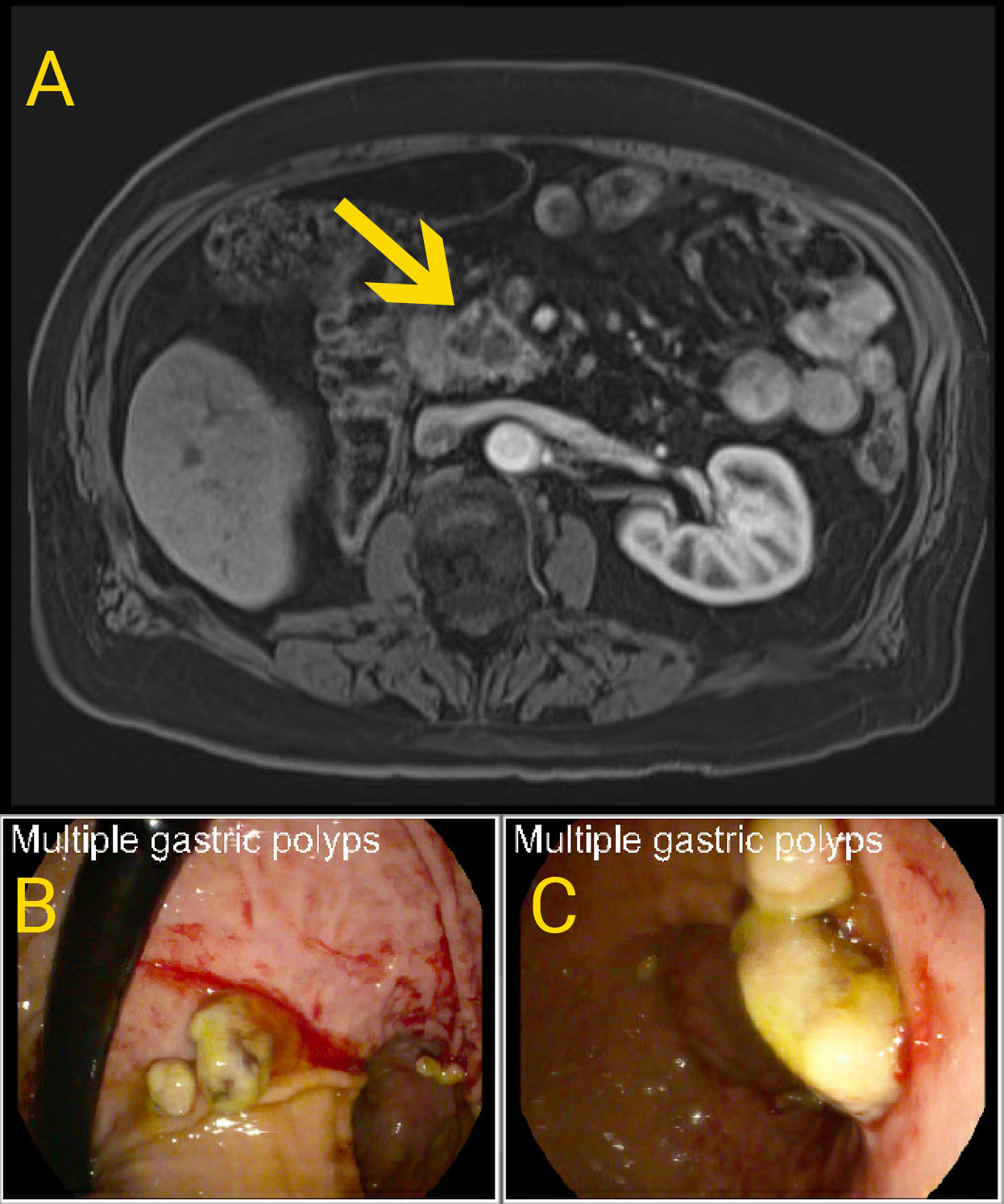
Figure: A: MRI T1 Axial Imaging Demonstrating Pancreatic Head Mass (yellow arrow). B&C: Endoscopic Images Demonstrating Malignant Gastric Polyps.
Disclosures:
Ade Waterman indicated no relevant financial relationships. Srikar Reddy indicated no relevant financial relationships. Chalhoub Walid indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ade Waterman, MBChB, Srikar Reddy, MD, Chalhoub Walid, MD. P0084 - Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma With Unusual Spread to the Pancreas, Biliary System, Ampulla of Vater, and Stomach, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
December 2021
Findings: Significant biliary dilation proximal to distal duct narrowing.
Intervention: Pus and debris extraction; fully covered metal stent placed.
March 2024
Findings: Periampullary abnormal tissue growth, multiple gastric polyps.
Intervention: Stent removal; balloon sweep to remove sludge/debris.
Pathology: Gastric polyp biopsy revealed metastatic ccRCC.
Metastatic RCC with gastrointestinal involvement poses significant management challenges. Regular monitoring and timely interventions are crucial to manage complications and maintain patient quality of life.

Figure: A: MRI T1 Axial Imaging Demonstrating Pancreatic Head Mass (yellow arrow). B&C: Endoscopic Images Demonstrating Malignant Gastric Polyps.
Disclosures:
Ade Waterman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Srikar Reddy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Chalhoub Walid indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ade Waterman, MBChB, Srikar Reddy, MD, Chalhoub Walid, MD. P0084 - Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma With Unusual Spread to the Pancreas, Biliary System, Ampulla of Vater, and Stomach, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.

